Why Choose Oil and Gas Software in the Energy Industry
Oil and gas software, a class of sophisticated programs and technologies, has transformed the way businesses explore, extract, manage, and optimize their operations. Oil and gas software is transforming the industry's future by reducing complex procedures and improving decision-making. In this post, we will look at the key aspects of oil and gas software and its impact on the energy industry.
What are the Functions of Oil and Gas Software
Oil and gas software comprises a wide range of solutions designed to solve the industry's unique difficulties. These applications cover everything from exploration and drilling to manufacturing, transportation, and distribution.
1. Exploration and Reservoir Modeling
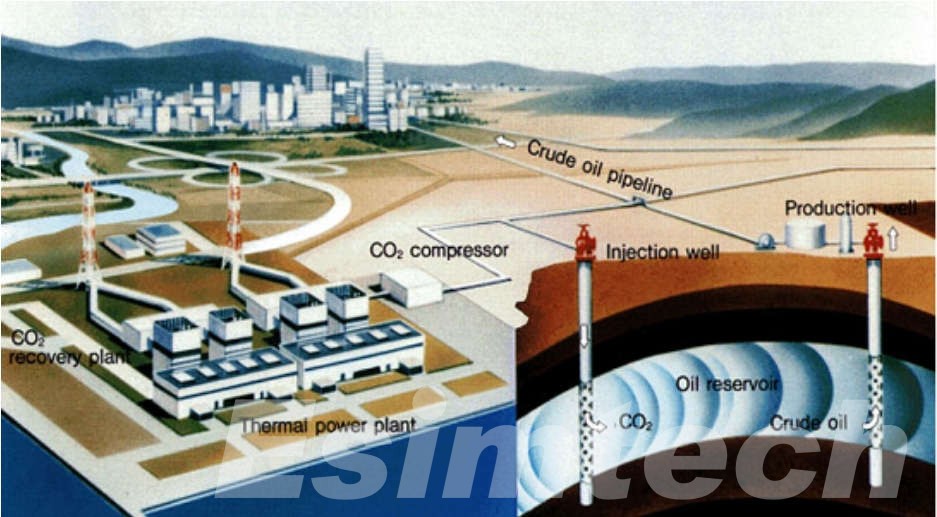
Advanced software helps geologists and geophysicists analyze seismic data, create 3D models of reservoirs, and simulate various drilling scenarios. This predictive power contributes in the identification of possible reserves, the estimation of production rates, and the optimization of drilling strategies.

2. Drilling and Well Management
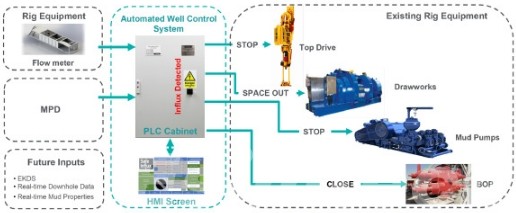
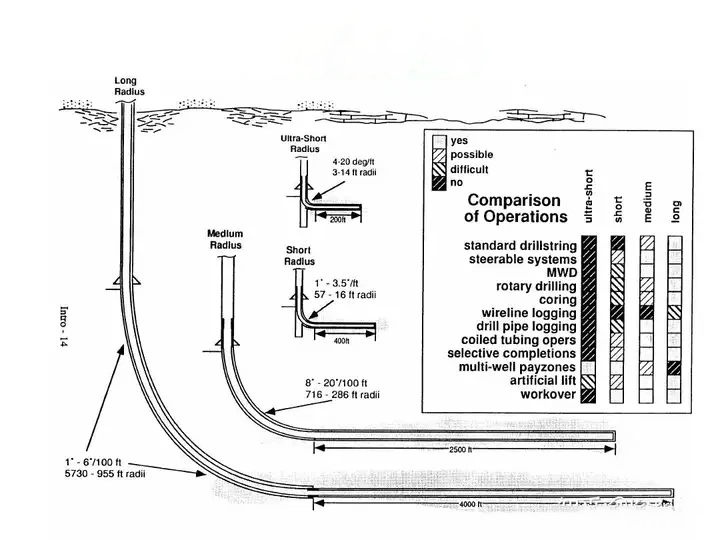
Drilling software aids engineers in precisely planning and carrying out drilling operations. It offers real-time data on well conditions, allowing modifications to be made to maximize drilling efficiency and well integrity.
3. Production Optimization
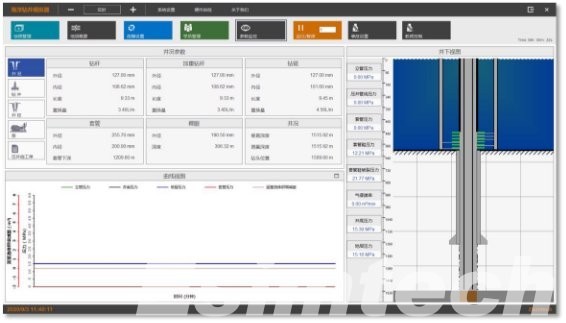
Production management software monitors the operation of wells and facilities, allowing anomalies to be detected and maintenance needs to be predicted. This results in less downtime and improved overall operational efficiency.
4. Data Analytics and Integration
Big data and analytics software processes massive volumes of operational data, providing insights that lead to more informed decisions. Data integration from several sources enhances visibility throughout the value chain, from discovery to distribution.
5. Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance software guarantees that operations follow environmental and safety rules. It monitors emissions, waste disposal, and other compliance-related elements in order to reduce the industry's environmental imprint.
What are the Advantages of Oil and Gas Software
The adoption of oil and gas software brings forth numerous benefitsthat influence the industry's efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
1. Efficiency and Cost Savings
Automation of manual operations and workflow optimization leads to increased efficiency, lower operational costs, and speedier decision-making. Predictive analytics aid in the prevention of equipment failures, reducing downtime.
2. Safety Enhancement
Real-time monitoring and data analysis improve safety by detecting possible threats and enabling for quick intervention. This decreases the possibility of accidents and assures the safety of workers.
3. Environmental Stewardship
Companies can reduce their environmental effect by using software tools for environmental monitoring and compliance. This leads to a more environmentally friendly approach to energy extraction and production.
4. Decision-Making Precision
Access to precise, real-time data enables decision-makers to react quickly to changing situations and make well-informed decisions that improve operations.
5. Collaboration and Communication
Collaboration software facilitates effective cooperation and knowledge exchange by enabling smooth communication and information sharing between teams, departments, and even partner businesses.
Challenges and Future Directions of Oil and Gas Software
The oil and gas business is undergoing a digital transition, which is being fueled by cutting-edge software solutions. While these improvements provide several advantages, they also raise issues that the business must solve.
Challenges in Oil and Gas Software Implementation
1. Integration Complexity
Many interrelated systems and processes are involved in oil and gas operations. Integrating new software with current infrastructure can be difficult and time-consuming, necessitating careful planning to assure compatibility and data consistency across the enterprise.
2. Data Management
The industry creates massive amounts of data from a variety of sources, including sensors, drilling operations, and manufacturing facilities. Managing, storing, and analyzing this data effectively is a problem that necessitates strong data management systems.
3. Data Security
The risk of cyberattacks and data breaches grows as software solutions become more linked. Protecting sensitive operational and proprietary data is critical for maintaining operational integrity and protecting against potential attacks.
4. Change Management
Introducing new software frequently necessitates a culture shift within the firm. Employees must adjust to new technologies and workflows, which may face opposition. To enable smooth transitions, effective change management practices are essential.

Future Directions in Oil and Gas Software
1. Advanced Data Analytics
The potential of data analytics holds the key to the future of oil and gas software. Real-time data can be processed by predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms to optimize drilling operations, detect equipment breakdowns, and increase overall efficiency.
2. Cloud Computing and IoT
Cloud-based solutions and the Internet of Things (IoT) will play an important role. Remote asset monitoring, real-time collaboration, and data availability from anywhere will improve decision-making and operational agility.
3. Digital Twin Technology
Using digital twin technology, virtual simulating of physical assets is created. This allows oil and gas simulator analyzing real-world scenarios, in order to make accurate predictions regarding equipment behavior and performance.

4. Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are revolutionizing several industries. Autonomous drilling rigs, robotic pipeline inspection, and remote-controlled vehicles for offshore operations are becoming increasingly common, improving safety and efficiency.
5. Blockchain Applications
In the oil and gas supply chain, blockchain technology can improve transparency, traceability, and security. Smart contracts have the potential to simplify transactions and eliminate conflicts, while secure data exchange has the potential to improve stakeholder engagement.
6. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
These innovations have the potential to transform training, maintenance, and remote help. Immersive training experiences can be provided using Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) and field technicians can receive real-time instruction from specialists.

Conclusion
Oil and gas software has evolved as a critical aspect of energy industry innovation. The software solutions will play an essential role in building a more efficient, safe, and sustainable energy future. As technology advances, the incorporation of modern software will likely play a critical part in determining the success of energy companies worldwide.