How to do Well in Offshore Oil Rig Decommissioning: What are Challenges and Strategies and How Simulation Technology Used for It
Offshore oil rig decommissioning poses a complicated set of issues that necessitate careful planning, respect to rules, and innovative ways to ensure environmental sustainability. As oil fields reach the end of their useful life, the decommissioning process becomes increasingly important. In this article, we explore the challenges associated with decommissioning offshore oil rigs, the strategies employed to overcome these hurdles and how simulation technology used in offshore oil rig decommissioning.
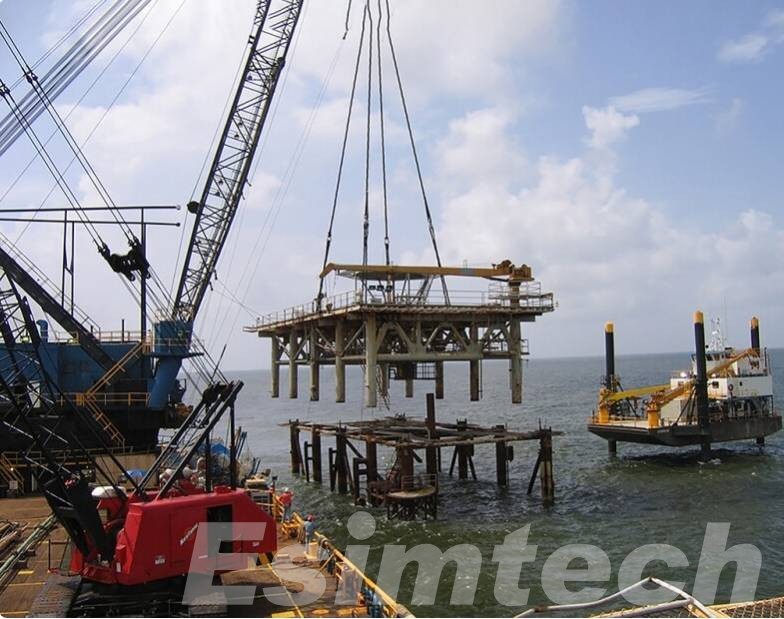

Challenges in Offshore Oil Rig Decommissioning
1. Regulatory Compliance
Meeting severe environmental standards is a major challenge in the decommissioning of offshore oil rigs. Regulatory agencies enforce tight rules to reduce environmental effect, maintain worker safety, and promote responsible equipment disposal.
2. Environmental Impact
Decommissioning activities have the potential to impact marine ecosystems. Proper disposal of materials, removal of contaminants, and mitigation of potential leaks or spills are critical to minimizing the environmental impact of decommissioning oil rigs.
3. Technological Complexity
Offshore oil rigs are equipped with intricate infrastructure, and decommissioning involves dismantling and removing these complex systems. Developing and employing advanced technologies for safe and efficient decommissioning poses a significant challenge.
4. Cost Management
Decommissioning is an expensive operation, and effectively anticipating and managing expenses is a constant issue. Cost overruns can be caused by unexpected challenges, changing market conditions, and evolving regulatory requirements.
5. Stakeholder Coordination
Multiple stakeholders, including government agencies, environmental groups, and the energy industry. It is critical for successful decommissioning programs to have efficient communication and coordination among these varied parties.
6. Worker Safety
Offshore decommissioning may include hazardous tasks. The safety of personnel during the dismantling and removal activities, which are frequently carried out in hazardous offshore settings, is a top priority.
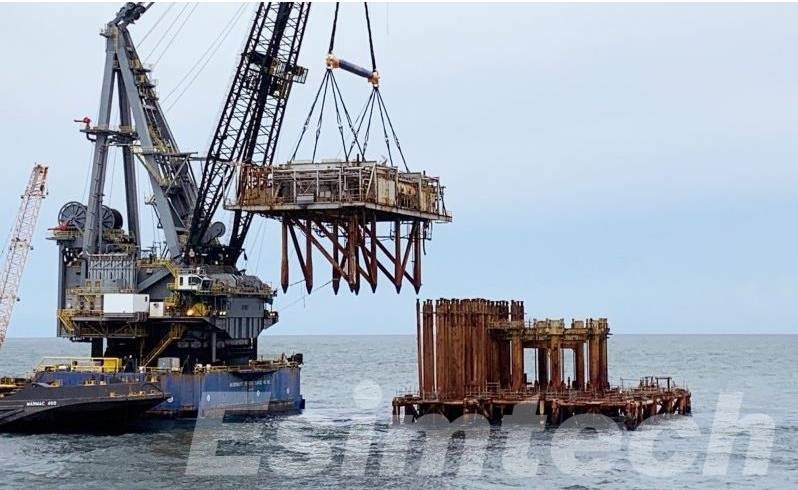

Strategies for Successful Offshore Oil Rig Decommissioning
1. Early Planning and Collaboration
Initiating the decommissioning planning process early in the life cycle of an oil field allows for better preparation and resource allocation. Collaborating with regulatory bodies and stakeholders ensures a comprehensive understanding of expectations and facilitates smoother execution.
2. Technological Innovation
Leveraging cutting-edge technologies, such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), artificial intelligence, and advanced robotics, can enhance the efficiency and safety of decommissioning processes. These technologies enable precise and controlled operations, minimizing environmental impact.
3. Rigorous Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with regulatory obligations is not negotiable. Environmental requirements, worker safety practices, and legal obligations are all met through strict compliance. Engaging with regulatory organizations throughout the process aids in the acquisition of required approvals and permits.
4. Environmental Impact Assessments
Conducting comprehensive environmental impact assessments before to and during decommissioning enables the proactive identification and mitigation of any environmental problems. These assessments can be used to establish waste disposal, habitat restoration, and pollution control strategies.
5. Financial Planning and Risk Management
Implementing robust financial planning and risk management practices helps anticipate and mitigate potential cost overruns. Establishing contingency funds and regularly reviewing financial plans in light of changing circumstances contribute to effective cost management.
6. Stakeholder Engagement
Open and transparent communication with all stakeholders is essential. Engaging with local communities, environmental groups, and industry partners fosters understanding, cooperation, and support for decommissioning initiatives. Regular updates and public consultations can address concerns and build trust.
7. Training and Safety Measures
Investing in comprehensive training programs for workers involved in decommissioning activities is critical. Implementing strict safety measures, emergency response protocols, and continuous monitoring contribute to a secure working environment.
8. Research and Development
Continuous R&D efforts in decommissioning technologies and processes are critical. Decommissioning methods that are more efficient, cost-effective, and ecologically benign might result from innovation.
How Simulation Technology Used in Offshore Oil Rig Decommissioning
Simulation technology is critical in offshore oil rig decommissioning because it creates a virtual environment in which to replicate and examine various components of the decommissioning process. This innovative technology is used at many stages of decommissioning, providing a variety of benefits ranging from planning and design to training and risk mitigation.
1. Rig Design and Planning
Virtual Prototyping: During the planning phase, engineers might use simulation to construct virtual prototypes of the rig and its components. This allows for the testing of various decommissioning situations and aids in the optimization of the dismantling and removal operations.
Structural Integrity Testing: Simulation technology assesses the structural integrity of the rig components, ensuring that the decommissioning plan considers the load-bearing capacity and potential challenges associated with dismantling.
2. Buoyancy and Stability Analysis
Hydrodynamic Simulation: Simulations help in understanding how the rig maintains buoyancy and stability in different sea conditions. By modeling the rig’s structure, ballast systems, and the surrounding environment, engineers can ensure that the rig remains stable during decommissioning operations.
3. Drilling Processes
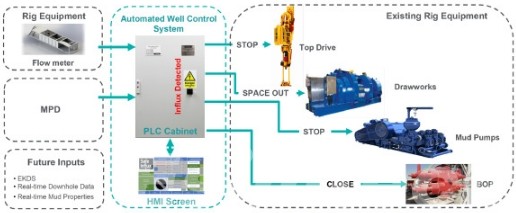
Drilling Simulations: Drilling and well control simulations allow rigs with infrastructure to practice and optimize well plugging and abandonment operations. This includes simulating plug insertion, cementing procedures, and well sealing to prevent environmental dangers.
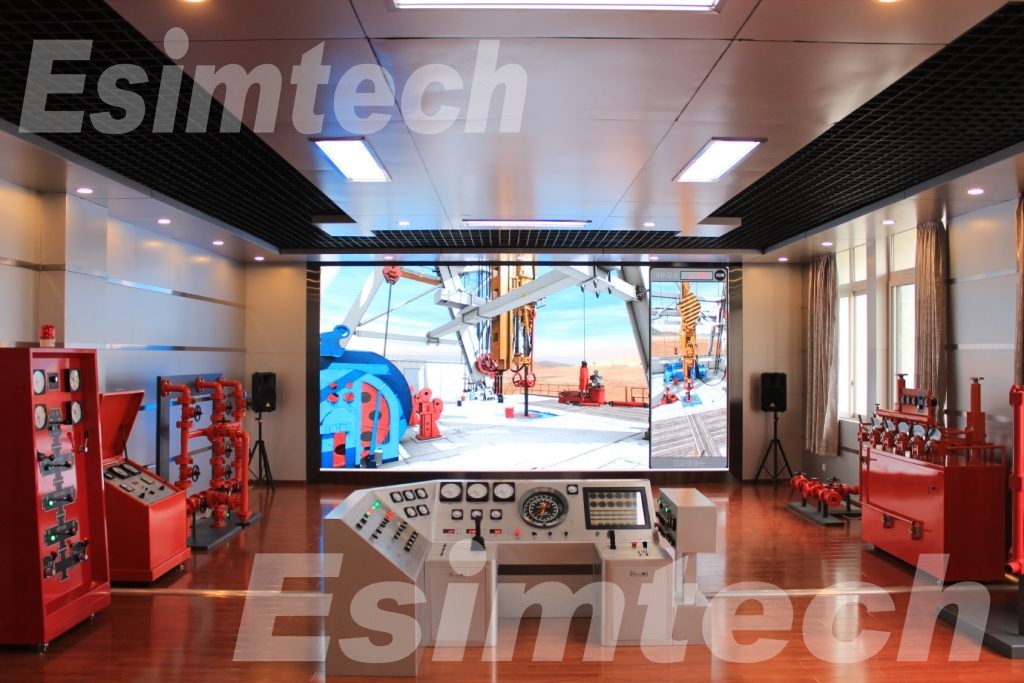

4. Dynamic Responses
Environmental Force Simulation: The responses of the rig to numerous dynamic elements such as waves, wind, and currents are simulated. This aids in forecasting how the rig's stability, mobility, and overall performance will be affected by these external forces during decommissioning.
5. Emergency Scenarios
Emergency Response Training: Simulators are used to train staff in emergency situations such as blowouts and fires. In a controlled virtual setting, crew members can rehearse evacuation procedures, well control measures, and other vital safety processes.
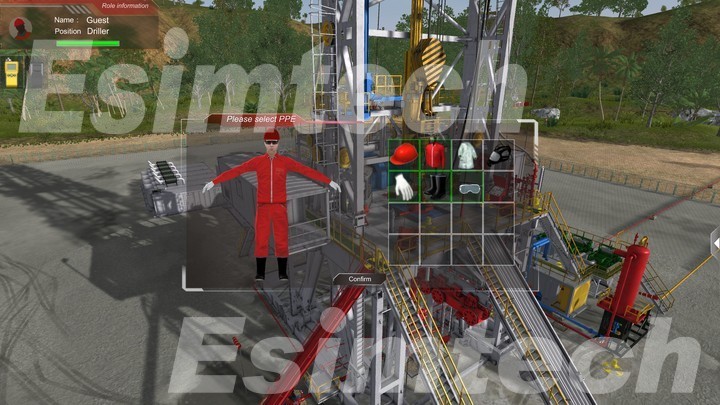

6. Crew Training
Virtual Reality (VR) Simulations: Advanced virtual reality simulations provide realistic training experiences for rig personnel. New recruits can familiarize themselves with decommissioning operations, equipment handling, and safety procedures before stepping onto the physical rig.
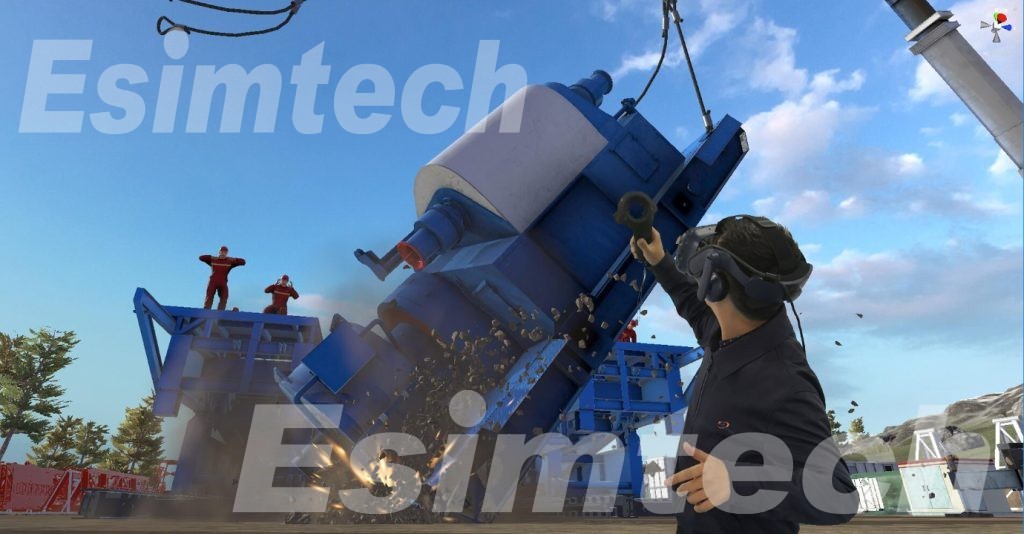

7. Equipment Testing
Machinery Performance Simulation: Simulation allows for testing and optimizing the performance of decommissioning equipment, cranes, and other machinery. Engineers can assess how different equipment configurations affect operations and identify potential issues before they occur on the actual rig.
8. Data Integration
Real-Time Data Feeds: Simulation platforms can be connected to real-time data feeds from operational rigs. This integration enables operators to make decisions based on actual data and respond to changing conditions in the virtual environment.
9. Optimization and Efficiency
Scenario Analysis: Through simulation, engineers can analyze different scenarios to identify opportunities for improving operational efficiency. This includes evaluating strategies for dismantling, waste disposal, and overall project management.
10. Risk Mitigation
Risk Assessment Simulations: Simulations help identify potential risks and challenges associated with rig decommissioning. By testing various scenarios virtually, operators can develop strategies to mitigate risks and enhance safety measures.
11. Research and Development
Testing New Technologies: Simulation is an important tool for evaluating new technologies, equipment, and procedures before they are put into use on actual rigs. This speeds up the innovation process and lowers the risk of implementing innovative ideas.
Conclusion
Offshore oil rig decommissioning is a difficult task that necessitates a deliberate and collaborative approach. With its ability to produce realistic and controlled virtual environments, simulation technology substantially adds to the efficiency, safety, and success of offshore oil rig decommissioning initiatives. Using new techniques, embracing technical improvements, and encouraging open communication among stakeholders will all help to ensure successful and environmentally responsible decommissioning initiatives, assuring a sustainable future for offshore energy exploration and production.