Safety Training in Oil Transportation
Oil transportation, whether through pipelines, tankers, rail or road, is crucial in the global supply chain of energy. However, it also poses substantial risks for personnel, communities, and the environment. Transport accidents can result in massive spills, fires, and even explosions. Thus, comprehensive safety training is a critical element to ensure efficient, safe, and legally compliant oil transportation operations.

Why Safety Training is Crucial in Oil Transportation
For oil transportation, safety training isn't merely an administrative requirement, but is a crucial security measure that protects individuals, the environment and the long-term viability of the industry.

Protecting Human Life in High-Risk Environments
The workers who work in the field of oil transportation are in high-risk and complicated situations. They frequently work with toxic, flammable, or pressurized materials in extremely time-sensitive conditions. Safety training equips them with the expertise and understanding necessary to handle these substances in a safe manner and respond swiftly in the case of emergency. If the training is comprehensive and continuously up-to-date, it decreases the chance of injury or deaths resulting from the failure of equipment, operational mistakes or unforeseen events.
Preventing Environmental Disasters
Oil spills can result in long-lasting environmental damage, degrade water sources, and cause destruction to marine life. Training in safety can prevent environmental catastrophes by ensuring that the transporters and their support teams know how to safely transport, handle as well as store the oil. Training programs also train personnel to recognize early indications of leaks or mechanical problems and act quickly to limit and prevent any issues prior to them escalating.

Meeting Regulatory and Legal Requirements
International and national regulations that govern transporting oil are very strict and failure to comply could lead to severe fines, legal penalties and even suspension of operations. Safety training assures that all personnel are well-aware of most current standards that are set by regulatory agencies like those of the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the International Maritime Organization (IMO). The compliance of employees through education isn't only a legal requirement but is also an essential element of corporate accountability.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency and Reliability
Employees who have been trained are more efficient and confident in their job. They understand how operate equipment properly and adhere to safety guidelines and resolve potential issues promptly. This guarantees reduced delays, shorter downtime and lower risks of expensive accidents. Safety training creates a culture of discipline and preparedness, which results in smoother, more reliable transportation operations.
Strengthening Emergency Response and Preparedness
Despite best efforts, emergencies do happen. If it's a pipeline leak or a collision with an oil tanker the speed and efficacy of the response will determine the extent of the damages. Safety training equips workers with specific emergency procedures which include evacuation strategies, containment strategies and plans for communication. Regular exercises and simulations based on scenarios aid employees in absorbing these strategies to be able to act quickly under pressure.
Promoting a Culture of Safety and Accountability
Safety training goes beyond instructional content. It's a potent tool to influence the culture of a workplace. In a way, it emphasizes the importance of safety to everyone Training encourages accountability, transparency and continual improvement. Workers are more likely complain about near-misses, voice concerns, and be supportive of each other when safety is a part of the values and procedures of the company.

Key Components of Safety Training in Oil Transportation
The effectiveness of safety training in oil transportation lies in the ability it provides personnel with both conceptual knowledge and the practical skills required to handle risk throughout the transportation process.
1. Understanding Oil Properties and Associated Hazards
The most important aspect of safety training is to educate workers on the chemical and physical characteristics of crude oil as well as refined petroleum product. Employees must be aware of the potential for flammability, volatility corrosion, and adverse health effects of the substances they work with. This understanding will allow them to predict the way oil behaves in various situations and use the proper precautions to avoid incidents.
2. Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
Training should include a systematic approach on identifying hazards that could be present in the transportation environment, such as valve leaks, valve failures or mechanical failures, as well as environmental conditions that may increase the risk. Workers learn to conduct risk assessments, analyze the likelihood and severity of accidents, and establish procedures to limit or eliminate risks before them causing incidents.
3. Safe Handling and Transportation Procedures
When loading pipelines or running a road tanker and managing offloading marine systems safety training must include clear guidelines to ensure safe handling. This includes guidelines for filling tanks grounding, pressure control, bonding procedures, as well as securing cargo. An understanding of how to handle the cargo reduces the chance of equipment failure, spills and exposure.

4. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The proper wearing of personal protective equipment (PPE) is an essential protection against injury and exposure. Safety training teaches the proper PPE to use, including gloves, clothing that is flame-resistant, goggles, hard hats, and respiratory protection based on the job and hazard degree. The employees are taught how to wear their PPE safely, as well as inspect and maintain their PPE, and then remove PPE for maximum efficiency.

5. Emergency Response and Spill Containment
The most important aspects of safety training is the ability to train workers to be able to effectively respond to emergency situations. This includes techniques for containing spills as well as firefighting strategies as well as first aid procedures as well as emergency communications and evacuation procedures. Regular drills simulate real-life scenarios that allow people to practice their role in controlled, timed environments. A quick, coordinated response could dramatically reduce the severity on an accident.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
A strict set of national, local and international laws governs transportation of oil. Training should cover pertinent laws, including those governed by the Hazardous Materials Transportation Act MARPOL (for protection against marine pollutants) as well as OSHA standards. Employees are also taught about the required documentation as well as procedures for reporting, which are crucial for investigations, audits, and ensuring legal compliance.
7. Communication and Safety Culture Development
Communication that is consistent and constant is crucial to security. Training will teach you the importance of reporting unsafe conditions as well as how to communicate during emergencies and observe chain-of command protocols. Furthermore, encouraging the safety-first mindset -- where people are encouraged and urged to speak out and actively identify hazards--is an essential component of the program. A well-established safety culture results in greater awareness and reduced incidents.
8. Technology Integration and Digital Safety Tools
Modern safety education also provides instruction in using digital tools, such as real-time monitoring systems, automatic alerts mobile safety apps and remote platforms for training. These tools improve awareness of the environment and provide information that can be utilized to continually improve security practices. Workers should be able to navigate these devices as part of their routine activities.
9. Ongoing Learning and Competency Assessments
A successful safety program is not an event that happens once. Continuous education, regular refresher classes, and renewals of certifications ensure that employees are proficient and current with the latest technology, emerging threats, and the latest regulations. Continuous evaluation also helps to determine knowledge gaps and customize training according to the needs of your business.

Why Use Simulation Technology for Enhancing Safety Training in Oil Transportation
Traditional safety training methods, like classes and on-the-job mentoring are vital, but they are often inadequate in their ability to prepare workers fully for the complicated, dangerous and unpredictable scenarios they may encounter. Simulation technology has become an effective tool that allows for immersive, realistic and repeatable training experiences that significantly improve safety outcomes in oil transportation.
1. Creating Realistic, Risk-Free Training Environments
Oil simulation technology lets students test high-risk procedures in a secure virtual space. If it's dealing with a pipeline break or managing the aftermath of a tanker crash or handling dangerous materials in the event of a spill, simulation-based training mimics real-world situations without exposing workers to real risk. The hands-on approach to learning helps improve the ability to make decisions under stress.
With 3D-based visualizations, Virtual Reality (VR) and interactive model, workers are able to be put in real-life situations where they are able to watch, interact, and react to changing emergencies or operational problems. This real-world experience helps employees learn safety procedures more efficiently than reading manuals or lectures on their own.

2. Enhancing Emergency Response Preparedness
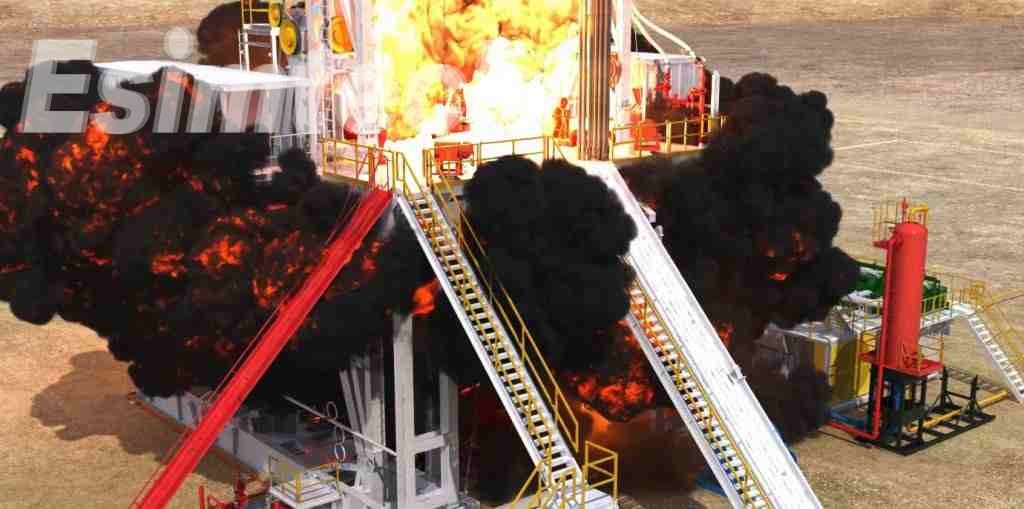
One of the most significant benefits that simulation technologies offer is their capacity to prepare personnel for emergency responses. Emergency training simulations can model complex emergencies, such as fires bursting out on tankers, leaks of toxic gas during oil transfer or derailments of oil-carrying trains, complete with alarms, time-sensitive choices and communication issues.
Trainees must perform the correct and immediate actions, including turning off emergency shut-off valves, installing spill containment equipment or coordinating evacuation plans. Repetition of these scenarios increases reflexes improves confidence, increases self-confidence, and minimizes the risk of human error in real emergencies.

3. Supporting Pipeline and Marine Transport Safety
Different modes of transportation, including ships, pipelines railcars, trucks and pipelines--pose distinct operational risk factors. Oil transportation simulators can be tailored to match the specific environment and equipment that are used in every mode. To aid pipeline managers, simulations reproduce the effects of pressure fluctuations, valve operation and alerts from monitoring systems. For mariners, simulations cover navigational hazards and pump system malfunctions and cargo management in dynamic oceans.
The role-specific simulations in these games assure that the learning is relevant, helping workers attain technical proficiency within their specific job roles and be prepared for the broader industry dangers.

4. Improving Team Coordination and Communication
The safety of oil transportation usually depends on coordinated actions between several team members, particularly during times of crisis. Simulation-based training exercises may include scenarios with multiple users where teams have to collaborate in real-time to spot issues, share information and develop a response plan. This enhances communication skills, clarifies chain of command responsibility, and fosters the development of a safety culture that is collaborative.
5. Enabling Performance Assessment and Feedback
Another benefit of the simulation technology lies in its ability to measure and monitor the performance. Simulations can gather data on the speed of reaction, accuracy of procedural procedures decisions, patterns of decision-making, and the adherence to protocols. Instructors can analyze these data points to give personalized feedback and suggest areas to improve.
This evidence-based assessment helps companies make sure that all employees meet safety standards prior to taking on crucial tasks on the job.
6. Reducing Training Costs and Operational Disruption
With the use of simulation in place of live equipment or field training exercises, organizations can cut down on the cost of operations and financial of training. There is no requirement to shut down pipelines or take vessels out of service. Trainees are able to learn repeatedly and at a high volume without interrupting actual operations, and all the without risking injury or damage while practicing.
Best Practices for Effective Safety Training in Oil Transport
| Best Practice | Description |
| Conduct Role-Specific Training | Customize safety-related content for every job role--drivers, pipeline operators, marine workers--so trainees are taught procedures that are relevant to their jobs. |
| Use Realistic Simulations | Integrate the use of virtual reality training simulations and scenario-based exercises and digital simulators to model operational and emergencies in real life. |
| Ensure Regulatory Alignment | Ensure that training programs are aligned with DOT, EPA, OSHA, and IMO requirements to ensure compliance with legal requirements and industry best practices. |
| Promote Continuous Learning | Refresher classes, micro-learning modules and regularly updated materials to refresh your knowledge and react to procedural or regulatory changes. |
| Encourage Active Participation | Make use of interactive tools for training, hands-on exercises and team-based exercises, to maintain engagement and improve retention. |
| Incorporate Emergency Response Training | Training workers on spill containment and evacuation procedures as well as firefighting and emergency communication in order to ensure quick and effective response during emergencies. |
| Assess and Certify Competency | Perform evaluations, track performance and certificates to confirm that students have mastered the necessary safety techniques prior to operating on their own. |
| Foster a Safety Culture | Encourage the open reporting of risks as well as near-misses and feedback in order to foster an awareness of the safety responsibilities at all levels of the workforce. |

Final Thoughts
In the highly risky world of oil transportation, safety training is essential. It helps protect lives, safeguards the environment, guarantees regulatory compliance, etc. Through investing in robust, role-specific, and frequently updated safety training programs, oil transportation companies can efficiently manage risk and operate confidently in a complex, challenging global energy supply chain.