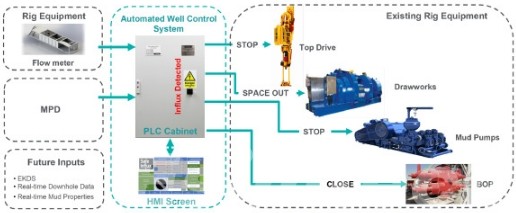
What are Annular BOP and Ram BOP: Functions, Comparison and Advantages Used in Simulation
In the realm of oil and gas drilling, ensuring safety takes precedence above all else. At the heart of safety measures in drilling operations stands the Blowout Preventer (BOP). Its purpose is to safeguard against the disastrous consequences of uncontrolled oil or gas releases from the well, known as blowouts. Within drilling operations, two primary categories of BOPs find extensive use: annular BOPs and ram BOPs. This article delves into the nuances of these two BOP types, shedding light on their distinct characteristics and the scenarios where their application is most fitting.

Functions of Annular BOP and Ram BOP
Annular BOP
Annular Blowout Preventers, often called annular BOPs, derive their name from their sealing method, which functions within the annular space between the wellbore and the drill pipe or casing. These BOPs provide a versatile well control solution, thanks to their capacity to conform to various pipe sizes and irregular wellbore shapes.
Key Features of Annular BOPs
- Flexible Sealing Element
The hallmark feature of annular BOPs is their use of a flexible rubber element, known as the packing unit. When activated, this packing unit is compressed, forming a tight seal around the drill pipe or casing. This flexibility allows annular BOPs to seal effectively around various pipe sizes.
- Adaptability
Annular BOPs are well-suited for situations where the wellbore geometry is irregular or when drilling through formations with varying shapes. The flexibility of the sealing element enables them to create a reliable seal, even in non-standard wellbore conditions.
- Ease of Maintenance
Maintenance of annular BOPs is often more straightforward compared to ram BOPs. The rubber packing unit can be replaced or repaired relatively easily, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Applications of Annular BOPs
- Drilling Operations: Annular BOPs are commonly used during drilling operations to control wellbore pressure and provide a seal around the drill pipe.
- Well Control: Annular BOPs play a crucial role in well control systems, acting as a backup measure to prevent blowouts.
- Circulation: They can be used for wellbore fluid circulation, allowing mud and other fluids to be circulated down the drill pipe and back up the annulus.
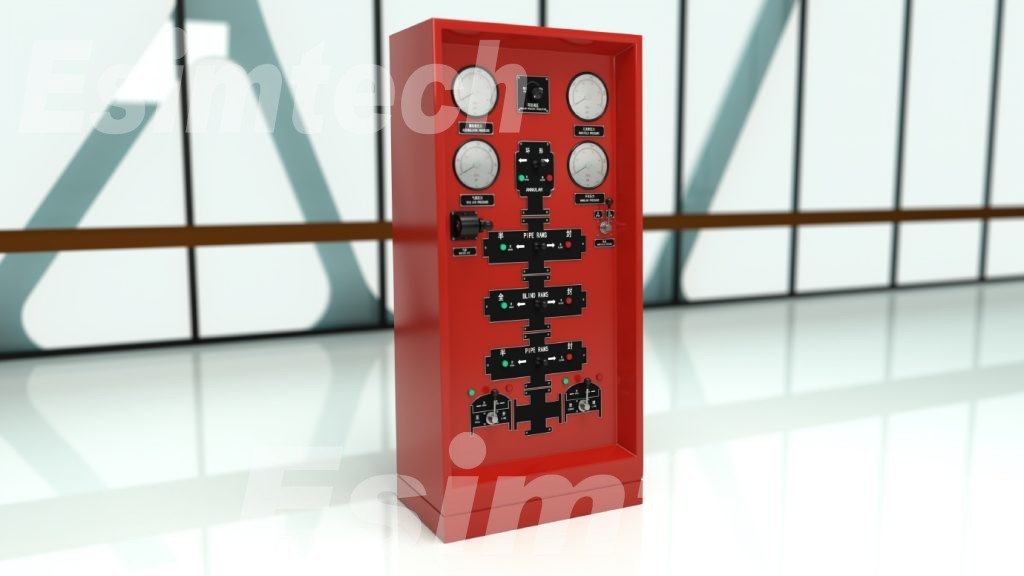

Ram BOP
Ram Blowout Preventers, also known as ram BOPs, utilize metal blades or rams to establish a tight seal around the drill pipe or casing. In contrast to annular BOPs, ram BOPs excel in delivering precise sealing and are frequently employed as a secondary well control safeguard, particularly during critical situations.
Key Features of Ram BOPs
- Sealing Mechanism
Ram BOPs use metal rams to create a seal. These rams can be configured for different purposes, such as sealing around the drill pipe or casing, cutting and sealing the pipe in emergencies, or creating a complete seal when no pipe is present.
- Specialized Configurations
Ram BOPs come in several specialized configurations:
- Blind Rams: Used to provide a complete seal when no pipe is present in the wellbore.
- Pipe Rams: Designed to seal around the drill pipe or casing, with various sizes available to accommodate different pipe diameters.
- Shear Rams: Specialized rams designed to cut and seal the drill pipe or casing in case of a well-control emergency.
- Variable Rams: Some ram BOPs have variable ram configurations that can adapt to different pipe sizes, providing flexibility during drilling operations.
- Reliability: Ram BOPs are known for their reliability and are often used as the last line of defense in a well-control system. They provide a robust and immediate seal, especially in emergencies.

Applications of Ram BOPs
- Emergency Well Control: Ram BOPs are often considered the last line of defense in well control systems. They are deployed in emergencies to quickly and precisely seal off the wellbore.
- Deepwater Drilling: In deepwater drilling operations where the consequences of a blowout can be catastrophic, ram BOPs, including shear rams, are crucial for maintaining control over the well.
- Ensuring Well Integrity: Ram BOPs play a critical role in ensuring the integrity of the well, especially when dealing with challenging formations or high-pressure zones.
Comparison Between Annular BOP and Ram BOP
While both BOP serve the same fundamental purpose of well control, they have different designs and functions. Here's a comparison between annular and ram BOPs:
1. Design and Function
Annular BOP: An annular BOP features a circular, doughnut-shaped rubber component that can encircle the drill pipe, casing, or other tubular elements within the wellbore. It achieves a seal by exerting pressure on the wellbore's inner diameter, rendering it adaptable for a range of pipe sizes. Its primary role is to seal off sections of the wellbore with irregular shapes or tapering dimensions.
Ram BOP: Ram BOPs comprise two steel plates, referred to as rams, which either converge horizontally or vertically to create a hermetic seal within the wellbore. These BOPs are meticulously engineered to offer a precise and robust sealing mechanism, making them the preferred choice for specific pipe sizes or scenarios demanding meticulous control.
2. Sealing Mechanism
Annular BOP: Annular BOPs use a flexible rubber element to seal around the pipe, providing a dynamic and adaptable seal. This flexibility allows them to accommodate variations in pipe size and shape.
Ram BOP: Ram BOPs use rigid steel plates (rams) to close around the pipe, providing a more rigid and fixed seal. They are generally more reliable for high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.

3. Applications
Annular BOP: Annular BOPs are frequently employed as the primary safeguard in drilling operations, particularly when handling diverse pipe sizes or contending with a non-standard wellbore configuration. Additionally, they find utility in well testing and wireline operations.
Ram BOP: Ram BOPs are commonly designated as secondary or contingency BOPs, typically coming into play when a precise, high-integrity seal is imperative, such as in emergency well control scenarios. They are also applied in instances necessitating the shearing or cutting of the drill pipe.
4. Maintenance
Annular BOP: Annular BOPs are generally easier to maintain and repair due to their simpler design and use of elastomeric seals. However, the seals may wear out over time and need periodic replacement.
Ram BOP: Ram BOPs can be more complex to maintain and repair, as they involve mechanical components that require careful inspection and maintenance.
5. Cost
Annular BOP: Annular BOPs are often less expensive than ram BOPs, making them a cost-effective choice for certain drilling situations.
Ram BOP: Ram BOPs are typically more expensive due to their precision engineering and materials required for high-pressure applications.
In practical applications, annular and ram BOPs are frequently employed together within well control systems to ensure redundancy and enhance adaptability. The selection between these two types hinges on the particular drilling operation, the state of the wellbore, and the safety imperatives in place.
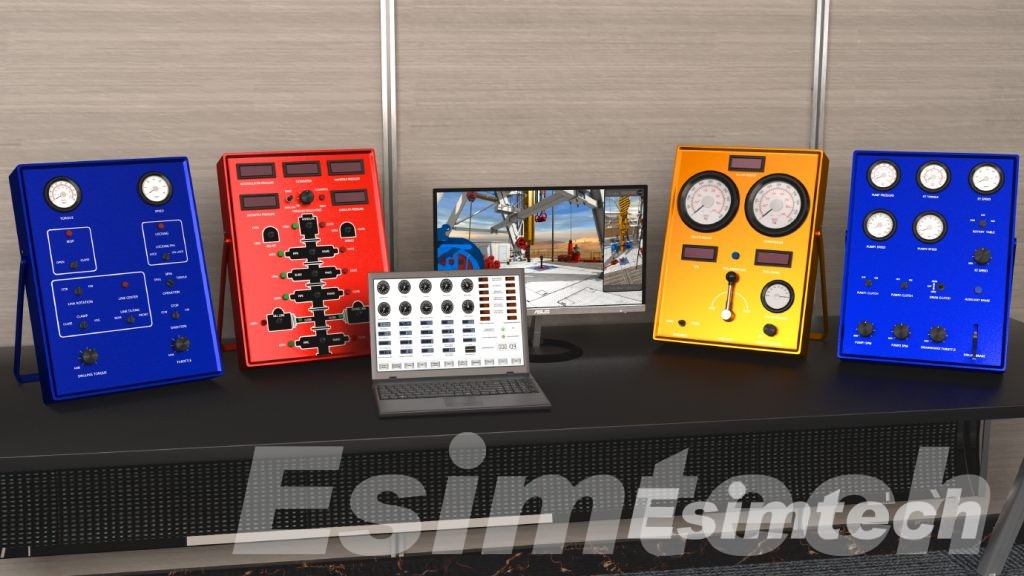

Advantages of Using Annular BOP and Ram BOP in Simulation
Simulation assumes a pivotal role in the decision-making process. Here are several pivotal advantages of using annular and ram BOPs in drilling and well control simulation systems.
- Performance Analysis
Simulations have the capability to replicate a wide array of drilling scenarios and conditions, enabling engineers and drilling operators to gauge the performance of annular BOPs and ram BOPs across diverse circumstances. This encompasses the assessment of their sealing effectiveness, response times, and pressure-holding capacities.
- Pressure and Flow Modeling
Through simulations, it becomes possible to precisely replicate pressure dynamics within both the wellbore and the BOP stack. Engineers can leverage this data to ascertain the necessary pressure rating for the BOP system and make informed decisions regarding whether an annular or ram BOP is the more appropriate choice for the anticipated pressure conditions during drilling.
- BOP Compatibility
Simulations can assess the compatibility of a particular BOP system with the wellbore design and drilling equipment. This helps ensure that the selected BOP type can effectively seal the well and control pressure during drilling operations.

- Dynamic Drilling Scenarios
Simulations can replicate dynamic drilling scenarios, including well kicks, wellbore instability, and unforeseen pressure surges. This capability enables drilling teams to assess the responses of each BOP type to these challenges and determine their effectiveness in promptly shutting in the well during emergency situations.
- Training and Preparedness
Simulations can be used for training drilling crews in the proper operation and response procedures for both annular and ram BOPs. This helps ensure that the drilling team is well-prepared for various well control scenarios.
- Risk Assessment
Simulations can be used to assess the risks associated with the choice of BOP type. This includes evaluating the probability of successful well control and the potential consequences of a BOP failure.

Conclusion
The choice between annular and ram BOPs depends on the specific drilling conditions, wellbore geometry, and safety requirements of a drilling operation. Both types of BOPs play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and integrity of oil and gas drilling operations, helping to prevent catastrophic blowouts and their associated environmental and human risks. We can use the power of simulators to select appropriate BOPs. Regardless of the choice, BOPs remain the frontline defense against well-control incidents, ensuring the safety of both personnel and the environment in the oil and gas industry.