Technological Advancements in Oil Rig Installation
Oil rig installation refers to the process of assembling and setting up structures designed for the exploration and extraction of oil and gas from beneath the Earth's surface. These installations are crucial components of the oil and gas industry, serving as platforms for drilling wells, extracting hydrocarbons, and managing the various processes involved in upstream operations. The installation of an oil rig involves intricate engineering, advanced technology, and skilled manpower. Offshore oil rig installations are commonly situated in deep-sea environments, where the exploration and extraction activities take place in challenging conditions. The process includes the deployment of drilling equipment, installation of production facilities, and implementation of safety measures to ensure the efficient and secure extraction of valuable resources from beneath the ocean floor.

Traditional Oil Rig Installation Methods
Traditional oil rig installation methods relied heavily on manual labor and large machinery, presenting inherent risks and limitations. Here's a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. Foundation Construction:
Shallow Waters: For rigs in shallow waters near coasts, foundations were often constructed using barges and pile drivers. Divers would manually hammer or drill piles into the seabed to create a stable base.
Deep Waters: For deeper waters, large jack-up barges would transport prefabricated foundation structures to the installation site. Once there, hydraulic legs would elevate the barge, allowing divers to weld the legs onto the seabed.
2. Platform Assembly:
Lifting Equipment: Massive cranes, either on barges or fixed platforms, lifted pre-built platform modules into place. Divers guided the modules and secured them through manual bolting and welding.
Welding and Inspection: Divers, often working in harsh underwater conditions, performed all welding and inspection tasks necessary for platform assembly.
3. Pipeline and Equipment Installation:
Subsea Infrastructure: Divers laid pipelines and umbilicals (control cables) on the seabed, connecting the platform to subsea wells. They manually performed pipe connections and installed additional underwater equipment.
Topside Infrastructure: Cranes lifted and installed topside equipment like drilling rigs, processing facilities, and accommodation modules onto the platform.
However, the traditional methods has its limitations:
- High Risk: Divers faced decompression sickness, drowning, and other hazards. Manual lifting and welding operations presented risks of accidents and injuries.
- Limited Efficiency: Manual processes were time-consuming and labor-intensive, increasing overall installation costs.
- Environmental Impact: Underwater activities could disrupt marine life and ecosystems.

Emerging Technologies in Oil Rig Installation
The traditional methods of oil rig installation, while effective, were often risky, inefficient, and had significant environmental impact. Thankfully, a wave of technological advancements is revolutionizing the field, offering exciting possibilities for safer, faster, and more sustainable practices. Here are some key emerging technologies shaping the future of oil rig installation.
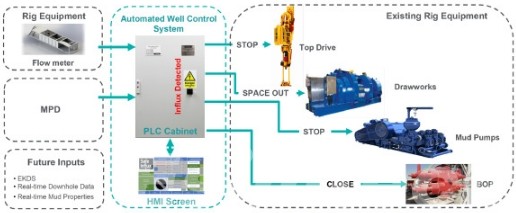
1. Robotics and Automation
The introduction of robots and automation is transforming the role of humans in oil rig installation. While this reduces risks associated with hazardous tasks like underwater welding, concerns regarding potential job displacement necessitate workforce upskilling and responsible transition strategies. However, the improved safety, efficiency, and consistency offered by automated systems remain noteworthy.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)
AI and ML algorithms are increasingly used to optimize installation processes and predict potential issues. Their ability to analyze vast data sets can lead to improved efficiency and reduced downtime. However, ethical considerations regarding algorithmic bias and data privacy should be addressed.

3. Advanced Materials
High-strength steel and composites offer lighter, stronger, and more durable rig components. This enables installation in previously inaccessible locations and potentially extends rig lifespans, reducing the environmental impact associated with frequent replacements. However, the environmental consequences of production and disposal of these materials necessitate careful evaluation.
4. 3D Printing
The potential of 3D printing to fabricate complex components on-site, reducing lead times and transportation needs, holds significant promise. However, the technology is still in its early stages and its feasibility and environmental impact require further assessment.
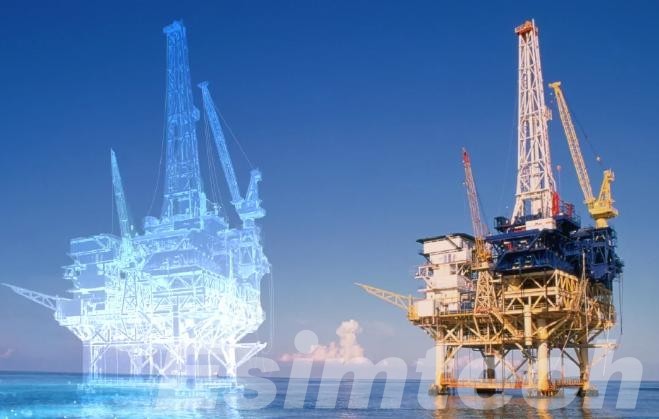

5. Digital Twins
Virtual replicas of real rigs, known as digital twins, allow for virtual testing and training, enhancing safety and efficiency. Additionally, real-time monitoring capabilities offer valuable insights and support informed decision-making. However, the security of data within these digital platforms remains a crucial consideration.
Benefits and Challenges of Emerging Technologies in Oil Rig Installation
The traditional methods of oil rig installation, while established, come with inherent risks and limitations. Emerging technologies offer exciting possibilities for a safer, more efficient, and potentially more sustainable future. However, embracing these advancements requires navigating a complex landscape of both benefits and challenges.
Benefits
- Enhancing Safety: Leveraging robotics in perilous activities, such as underwater welding, can mitigate the risk of injury or fatality for human workers. Additionally, the predictive capabilities of AI and ML technologies can foresee potential equipment failures, averting downtime and minimizing the occurrence of accidents.
- Boosting Efficiency: The integration of automation and optimized processes driven by AI and ML stands to markedly decrease both installation time and costs. Furthermore, the on-site application of 3D printing holds the potential to streamline logistics and fabrication processes, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- Promoting Sustainability: Incorporating advanced materials in rig construction can elongate the lifespan of rigs, diminishing the frequency of replacements and curbing their associated environmental impact. The implementation of digital twins offers the opportunity to fine-tune resource usage, minimizing waste and contributing to sustainable practices within the industry.
Challenges
- Financial Investment: The integration of these technologies demands substantial initial investments, which could pose a barrier for certain companies.
- Workforce Transition: The advent of automation may result in workforce displacement in specific sectors. It is imperative to implement upskilling and reskilling initiatives to facilitate a seamless transition for employees.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Existing regulations may need adjustments to accommodate the deployment of these new technologies, with a focus on ensuring safety standards and environmental protection.
- Ethical Considerations: The development and utilization of AI algorithms should adhere to ethical standards, addressing potential biases and concerns related to data privacy.
- Technological Maturation: Some technologies, such as 3D printing, are still in their early developmental phases. Further research and testing are essential to validate their reliability and feasibility in practical applications.
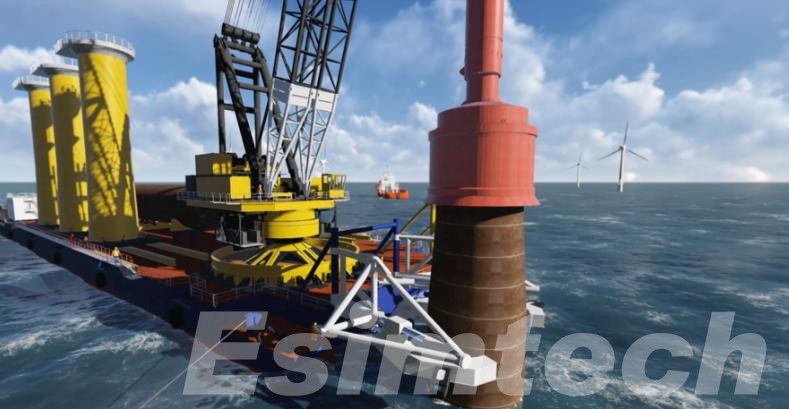

Oil Rig Installation Animation for Training
Oil rig installation animations have become instrumental in modern training programs, offering a dynamic and immersive learning experience. These animations create virtual environments that simulate the complexities of real-world rig installations, allowing trainees to navigate and interact with various components and procedures. The interactive nature of these animations facilitates hands-on learning, enabling trainees to comprehend the intricacies of oil rig assembly.
Moreover, scenario-based simulations help individuals practice decision-making and emergency response strategies in a risk-free virtual setting. From realistic equipment simulations to depicting safety protocols and emergency drills, these animations contribute to a comprehensive and standardized training experience. The benefits extend to cost-efficiency, as they eliminate the need for physical mock-ups, and to continuous learning, as the modules can be easily updated to reflect the latest advancements in technology and procedures. Therefore, oil rig installation animations enhance the competency, confidence, and safety awareness of personnel involved in the critical processes of rig deployment and maintenance.
Summary
Technological advancements in oil rig installation signify a paradigm shift in the industry, enhancing safety, efficiency, and sustainability. While challenges exist, the benefits of these innovations promise a future where oil rig installations are not only more reliable and cost-effective but also environmentally conscious. The integration of oil rig installation animations further contributes to shaping a skilled and adaptive workforce, prepared for the demands of the evolving oil and gas landscape.