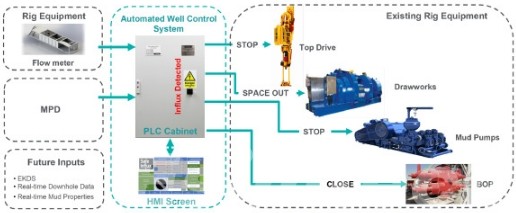
Wireline Logging in HPHT Wells: Challenges and Best Solutions
Wireline logging is essential in evaluating wells by providing high-resolution data about formation's properties, fluid content and well integrity. In High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) wells, the wireline logging becomes much more crucial and more complicated. These extreme environments, typically defined by pressures greater than 15,000 psi and temperatures exceeding 300°F (150°C), demand advanced tools, techniques and meticulous planning to ensure successful operations. This articles focuses on wireline logging in HPHT wells, including the challenges, solutions and future trends.

Understanding HPHT Well Environments
HPHT wells are often used in deep offshore as well as ultra-deep offshore drilling operations. They are often filled with important hydrocarbons, however their harsh environments create significant technical, operational and safety issues. The materials and equipment that are used in standard wells are often insufficient, which requires the use of specially developed wireline logging equipment that can stand up to extreme temperatures and pressure while ensuring data integrity.

Key Objectives of Wireline Logging in HPHT Wells
| Objective | Description |
| Formation Evaluation | Find porosity, permeability the lithology, and saturation of hydrocarbons during severe HPHT conditions. |
| Pressure and Temperature Profiling | Measure accurately downhole pressure and temperature in order to evaluate conditions in the well and to determine design completions. |
| Cased Hole Evaluation | Examine the quality of cement bonds Casing integrity, cement bond quality and reservoir depletion the completed HPHT wells. |
| Reservoir Fluid Sampling | Get high-quality PVT samples of formation fluid for and compositional analysis with HPHT restrictions. |
| Well Integrity Monitoring | Find issues such as leaks, corrosion or mechanical damage to keep the well in good health for the long term. the well. |

Challenges of Wireline Logging in HPHT Wells
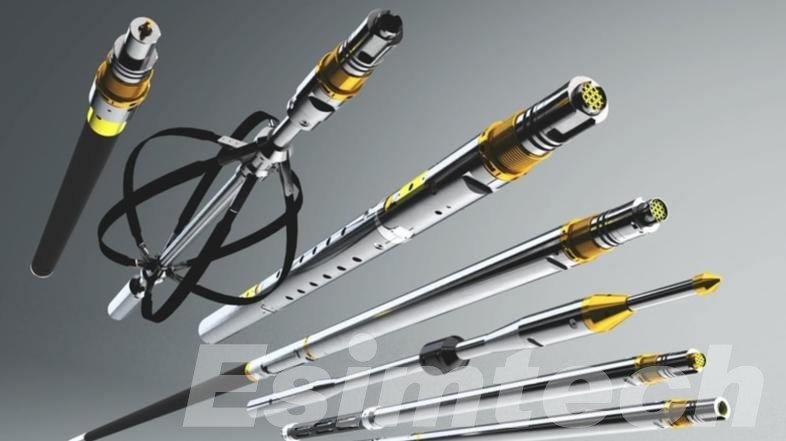
- Tool Integrity Under Extreme Conditions
HPHT wells expose wireline logging tools to temperatures frequently exceeding175°C and pressures over 20000 psi. Seals, electronics and structural parts could break or become damaged under these conditions. To prevent this from happening, tools should be designed using specific materials like Inconel, ceramic insulators, HPHT-rated elastomers which can keep their performance and accuracy in measurement regardless of mechanical and thermal stress.

- Data Transmission Reliability
In high-pressure, high temperature environments the transmission of data through the wireline cable can be difficult. The conductors' resistance is high in high temperatures as well as signal attenuation and electromagnetic interference may distort or delay the real-time information making it difficult to make well-sited decisions. High-strength, high-temperature cables as well as advanced technology for telemetry are needed to solve these problems.
- Increased Operational Risk and Safety Concerns
HPHT wells usually have limited operating pressure windows that are confined to the interstitial pressure as well as the fracture gradient, thereby increasing the likelihood of incidents involving well control when wireline deployment. Influxes of gas as well as tool sticking and cable failures can pose serious dangers for equipment and personnel. This is why thorough assessments of risk, real-time monitoring and contingency plans are vital to secure HPHT recording.
- Limited Availability of HPHT-certified Tools
The majority of wireline equipment is not certified for HPHT usage, which restricts the options available to the logging industry. The process of developing and certifying tools to work under HPHT conditions is expensive and time-consuming which limits flexibility and can lead to delays in operation when unexpected downhole conditions occur.
- Thermal and Mechanical Degradation Over Time
Long-term exposure HPHT conditions could lead to the gradual degrading of tools, specifically in seals, insulation materials or electronic component. The high load and the cycle of heat could also lead to the fatigue of metal or expansion of material decreasing the tool's reliability and accelerating the frequency of maintenance.
- Complex Logistics and Pre-Job Planning Requirements
Wireline operations in HPHT wells require careful planning and sophisticated modeling. Tool conditioning, thermal simulations strategies and operational scenario tests are required prior to the time of operation to ensure that tools work properly and that the log data is valid. These procedures require extra time and resources as well as expertise.

Solutions and Best Practices for Wireline Logging in HPHT Wells
1. Advanced Tool Design for Extreme Conditions
One of the most effective solutions to HPHT wireline logging is the creation of robust log tools. They are developed with high-performance alloys such as Inconel and titanium. These alloys are able to stand up to extreme pressure without bending. Electronics are enclosed in thermal insulation material, and the key components are constructed from HPHT-rated elastomers as well as ceramics to ensure stability over time. Innovative technologies like high-temperature batteries, solid-state memory and pressure-compensated housings increase the longevity of tools and their performance.
2. Deployment of HPHT-rated Cables and Connectors
High-specification log cables are essential to transmit power and data during HPHT conditions. They are made with a higher mechanical and thermal strength using copper conductors with high purity and thermally solid insulation materials like Teflon as well as PEEK. Specialized connectors and armor reinforced can reduce the loss of signal and fatigue in cables which allows for extended and more extensive deployment, with solid data transmission.
3. Use of Memory-based Logging Tools
In situations where the real-time telemetry system becomes unreliable or unpractical, memory-logging tools can be a viable alternative. They record data internally throughout the course of operation and can be used to post-process the data at the level. They are especially useful when wellbore conditions pose dangers or risks, as well as when cable communication is not able to be sustained for extended periods. Memory logs are critical to redundancy and guarantees the continuity of data acquisition in difficult HPHT conditions.

4. Precision Thermal Modeling and Pre-Job Planning
A precise thermal model is a essential element in efficient HPHT wireline operation. Engineers model expected downhole temperatures and pressures to determine how fluids and tools behave. The pre-job planning process includes setting pressure and temperature limits and identifying contingency plans, and determining the needs for conditioning of tools. This involves deciding on the appropriate deployment method including lubricators and pressure-control equipment specifically designed to HPHT wells.
5. Real-Time Monitoring and Adaptive Decision Making
Despite the difficulty of achieving continuous real-time telemetry under HPHT conditions, many HPHT operations have now incorporated advanced monitoring systems that monitor downhole parameters while the logging. Acoustic systems, digital telemetry along with high-speed processing of downholes permit operators to identify tools malfunctions, pressure fluctuations or wellbore instability in real-time. This method of adjusting improves security and allows for timely decision-making in critical logging runs.
6. Strict Adherence to Safety and Contingency Protocols
HPHT wireline operations come with inherent risks that have to be minimized by strict adhering to safety guidelines. Assessments of risk prior to job start and blowout preventer (BOP) configurations and emergency shutdown protocols are essential to any log-logging job. The personnel must be specially trained for HPHT scenarios and the equipment must contain fail-safes, such as weak points in cables and tool release mechanisms and remote control of pressure systems.
7. Cooperation with the Technology providers
Operators frequently depend on close collaboration with service companies to create custom logging programs that are suited to specific HPHT and well-conditions. These partnerships allow for an integration with cutting-edge technology and allow for field-specific calibration as well as access to technical assistance as well as support. The early engagement with technology suppliers assures that the equipment is appropriate and approved to work with HPHT operation.
8. Post-logging Analysis and Data Validation
Due to the cost and complex nature in HPHT wells, it is clear that the importance of wireline information cannot be overemphasized. After recording, data should be carefully checked to ensure accuracy and consistency. Specialized software tools aid in understanding characteristics of the formation, while also accounting for changes in temperature or signal attenuation. The accuracy of interpretation is essential to better making decisions regarding reservoir modeling, completion design and other future intervention.
How Simulations are Used for Wireline Logging in HPHT Wells
By using advanced oil and gas simulations, operators and service providers are able to identify challenges, develop robust tools and improve the process of decision-making before and during wireline logging operations.
Thermal and Mechanical Stress Modeling
One of the main applications that simulation technology can serve is simulate the mechanical and thermal stress that wireline equipment and cables encounter in HPHT deployments. Utilizing Finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) engineers can simulate temperatures and pressure loads on the wireline and downhole equipment. This allows them to predict potential sources of failure, for instance the electronics overheating or fatigued cables which allows design enhancements or operational adjustments prior to actually running.
Downhole Environment and Fluid Behavior Simulation
The accuracy of replicating the downhole environment in a virtual space is essential. Downhole operation simulations model the formation pressure and temperature, fluid flow, and chemical interactions to determine the impact of these variables on the performance of the tool in data capture. For instance, the properties of fluids such as density and viscosity under HPHT conditions can affect the logging of measurements like resistivity as well as audio signals. Simulation of these effects can help in the calibration of tools and refinement of algorithms to interpret data.

Tool Performance and Calibration Simulations
Prior to deployment, simulation tools simulate the way that specific wireline logging tools perform in HPHT conditions. This involves testing the sensor's response to signal attenuation, sensor response, and the behavior of tool electronics under the expected pressure and temperature profiles. Through conducting these tests virtual operators can calibrate the tools with precision, reducing uncertainty and increasing the accuracy of the information gathered.
Risk Assessment and Operational Planning
Emergency training simulation systems facilitates extensive risk assessments using various operational scenarios, such as tools deployment, retrieval and the possibility of failure. The simulation "what-if" analyses allow teams to spot potential hazards, like cable sticking tools overheating, cable sticking, as well as instability in the wellbore. These information can be used to plan contingency plans as well as equipment selection and the training of crew members, which contributes to more effective and safer cable logging.

Real-Time Data Integration and Decision Support
Advanced well logging simulation platforms can incorporate live data feeds throughout log operations to offer predictive analysis and real-time decision-making. When comparing measurements received with simulation models, operators are able to observe deviations that could be a sign of problems with the tool or even changes to the downhole. This method of dynamic simulation enhances awareness of the situation and aids in optimizing log runs in HPHT wells.

Training and Skill Development
Simulation environments provide beneficial training equipment for wireline operators and engineers who work in HPHT settings. VR (VR) and computer-based simulators model the complexity of HPHT log jobs which allows personnel to practice procedures as well as respond to emergency situations and learn about the behavior of equipment without the risk of live operations. This helps improve operational efficiency and safety.

Future Outlook of Wireline Logging in HPHT Wells
As exploration expands into more extreme reservoirs, it is expected that the future of wireline logs is shaped by advancements in the fields of materials technology, science and operational techniques. These innovations will improve the reliability of tools, data accuracy and safety while reducing costs and downtime.
- Enhanced Materials and Tool Durability
A new generation of wireline log tools will more often rely on cutting-edge materials that are able to withstand pressures up to 30000 psi as well as temperatures that exceed 400°F (204°C). Advancements in high-temperature electronics, advanced alloys, as well as nanomaterial coatings will increase the tool's durability and operational windows that will enable longer and more thorough log runs, without compromising the quality of data.
- Integration of Digital Twins and Predictive Analytics
Digital twin technology is expected to become an integral part of HPHT wireline logs. By constructing in real time virtual replicates of tools for logging as environments, the operators will be able to simulate and predict the behavior of the tool and optimize the parameters of logging and spot anomalies before they occur. In conjunction with machine learning and predictive analytics algorithms, this can enable proactive maintenance and better operational choices.

- Advanced Telemetry and Data Transmission Systems
The future telemetry systems will concentrate on increasing data bandwidth and transmitting reliability in difficult HPHT conditions. Innovative technologies like fiber-optic cables, acoustic and telemetry and wireless downhole communication are expected to minimize data loss and increase the ability to monitor in real-time, which allows to provide more accurate and immediate subsurface analysis.
- Increased Use of Autonomous and Memory Logging Tools
Autonomous wireline devices that have memory storage and onboard processing will be more widely used particularly in scenarios when real-time data transmission is constrained by environmental restrictions. These tools will provide greater adaptability and sturdiness, as well as capturing high-quality data that can be analysed in depth once it has been it is retrieved from the an appropriate location.
- Enhanced Simulation and Training Technologies
The role of simulation when designing and carrying out HPHT wireline logging activities will continue to expand, including augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to give operators an immersive training. These technologies can prepare employees for complex scenarios, increasing security and operational efficiency.

- Sustainability and Cost Efficiency
In the future, developments should concentrate on decreasing the environmental footprint and the overall cost of HPHT log operations. This involves optimizing design and tool designs to reduce the amount of the amount of time wasted through pre-planned maintenance, and implementing more efficient deployment techniques that use less energy.
- Collaborative Industry Innovation
Future developments in HPHT wireline logs will be characterized by greater collaboration between service providers, operators, and tech developers. Platforms for sharing data and joint research initiatives will boost the pace of innovation, resulting in more reliable, standardized and efficient log solutions for the most extreme conditions.
Summary
Wireline logging in HPHT wells is an essential element of sophisticated reservoir evaluation and well integrity monitoring. Despite its challenges, continual innovations and adherence to best practices are making these operations safer and more reliable.