Oil and Gas Data Management Software: Why It Matters
The oil and gas sector has reached a point where the effective handling of data has transformed from being a competitive edge to becoming a main operational requirement. The industry produces daily large amounts of data that are complex, high-speed, and difficult to handle coming from various sources such as seismic surveys, drilling logs, real-time production streams, and safety reports.
With the digital transformation process being accelerated, companies are introducing automation, remote operations, AI-driven analysis, and compliance frameworks that are tougher than before, which all leads to the main requirement for robust data management software. By the year 2025, organizations that are good at collecting, structuring, analyzing, and utilizing their data have started getting tangible benefits in terms of cost efficiency, operational accuracy, and risk demarcation.This article explores why advanced data management software is essential for modern oil and gas workflows, the challenges it solves, how it enhances operational accuracy, and the key criteria for selecting the right solution.
What Is Oil and Gas Data Management Software?
Oil and gas data management software refers to platforms designed to capture, store, process, visualize, and distribute technical and operational data across the upstream, midstream, and downstream segments.
These systems typically handle:
- Well logging and drilling data
- Geological and geophysical datasets
- Seismic imaging
- Production monitoring streams
- Asset performance and maintenance data
- Safety and compliance records
- Training and simulation outputs
Now modern data management platforms have created a way of dealing with and bringing together Separate data sets through a single central place. This way, they have also enabled the different departments like geoscience, engineering, and operations to collaborate with each other easily and with high quality throughout.
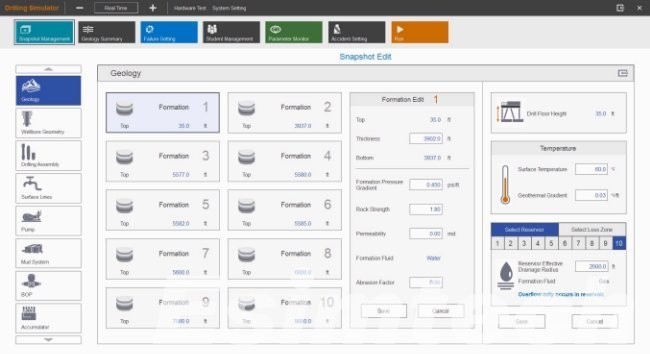
Key Challenges in Oil and Gas Data Management
Although the digital infrastructure has improved a lot, the industry still suffers from heavy data complexity. To relieve the burden modern software solutions directly tackle these issues.
1. High-volume and multi-format data
Oilfield data can come from different sources like LAS logs, SEGY seismic files, real-time monitoring, and imaging, all together with their various formats.
Also, manual handling can cause it to be mismatched, errored, or even lose some details.
2. Data silos across departments
Geologists, drillers, reservoir engineers, and operations still rely on different systems, which have a negative impact on visibility and lead to slower decision-making processes.
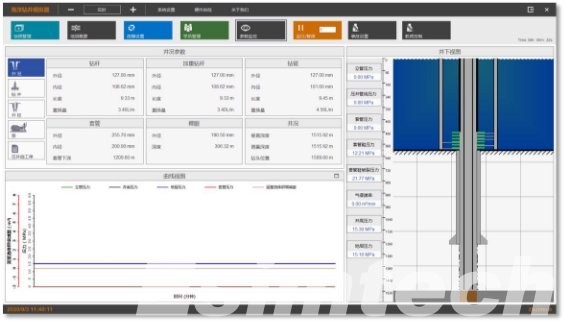
3. Inconsistent data quality
The presence of large-scale duplicates, incomplete data, or unstructured data can result in wrong analysis and thereby incorrect operational decisions.
4. Increasing compliance obligations
The rule makers will be imposing detailed traceability and reporting requirements across drilling, production, and environmental indicators in 2025.
5. Cybersecurity and data integrity risks
With the continuation of remote operations, it will be critical to maintain secure access to the data and protect the confidentiality of the data.
6. Rising operational costs
Poorly managed data workflows are the main cause of increased downtime, site visits that are not required, and elongation of evaluation cycles.

Benefits of Adopting Robust Data Management Software
1. Improved Data Quality and Standardization
The latest data management tools perform automatic cleaning, verification, and conversion of datasets, and all teams are thus working on the same reliable datasets.
Reduction in errors in well planning, geological modeling, and production forecasting is one of the direct results of this.
2. Faster and More Accurate Decision-Making
A unified data environment is one of the factors that enables the decision-makers to quickly access both historical and current information.
This is the case in drilling where the detection of hazards is hastened and the risk of non-productive time (NPT) is lowered.
3. Reduced Operational Costs
Through automation, manual data handling is reduced, field measurements are cut down, and the analysis cycle is shortened.
The cumulative effect of these factors is the incremental decrease in operational expenditure over time which becomes substantial.
4. Stronger Collaboration Across Technical Teams
A single platform for data and applications that enables seamless communication among geosciences, drilling, and production teams and departments.
5. Enhanced Compliance and Traceability
Modern solutions feature comprehensive audit trails, access control, and automated reporting capabilities to ensure compliance with the latest regulatory standards.
6. AI-Driven Insights and Predictive Capabilities
When organizations are using machine learning and predictive analytics in their business processes, the need for high-quality data is critical.
The data management software provides the necessary foundation that enables accurate modeling, optimization, and automated decision support.

Practical Use Cases in Real Oil & Gas Operations
Use Case 1: Well Logging Data Integration
Efficient data management ensures accurate interpretation of logging measurements, enabling better reservoir evaluation, porosity analysis, and hydrocarbon identification.
This is also where training platforms—such as ESIMTECH’s well logging simulation systems—support data standardization and interpretation accuracy through realistic learning environments.
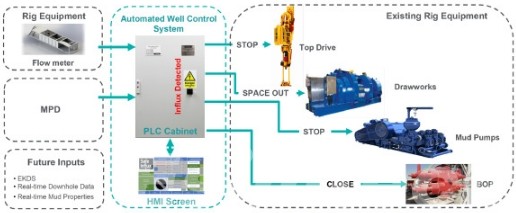
Use Case 2: Real-Time Drilling Data Monitoring
Advanced platforms consolidate MWD/LWD, telemetry, and rig-site sensor data for real-time oversight.
This allows drilling engineers to identify anomalies, optimize parameters, and prevent costly incidents.
Use Case 3: Production Optimization
Integrated production data helps identify flow irregularities, equipment degradation, and opportunities for enhanced oil recovery.
Use Case 4: Digital Twin and Modeling Applications
Accurate, structured datasets are crucial for supporting digital twin implementations, predictive maintenance, and AI-guided operational planning.
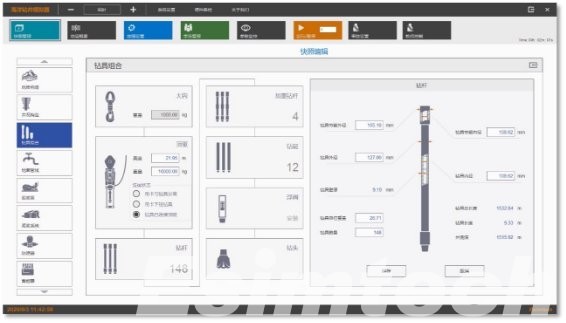
How to Choose the Right Oil and Gas Data Management Software
1. Comprehensive Multi-Format Data Integration
Support for seismic, logging, drilling, imaging, real-time telemetry, and historical datasets is essential.
2. Scalability for Different Organizational Sizes
The platform should support training institutions, small operators, and major oil companies alike.
3. Advanced Visualization Tools
High-resolution charts, 3D models, and interactive dashboards aid accurate interpretation.
4. Strong Compliance and Security Features
Audit logs, user permissions, encryption, and automated reporting are critical in 2025.
5. AI and Predictive Analytics Compatibility
The platform should enable integration with machine learning modules and digital twin environments.
6. Vendor Expertise and Industry-Specific Capabilities
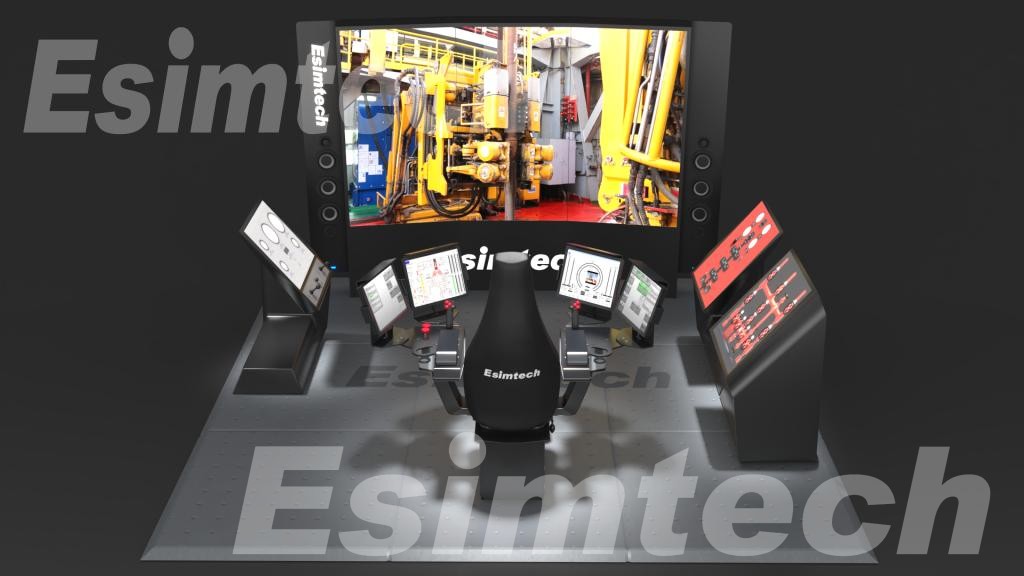
Vendors with oil and gas specialization—such as ESIMTECH, with decades of training and simulation experience—offer solutions grounded in real operational requirements.
How ESIMTECH Supports High-Quality Data Workflows
We provides advanced simulation and training solutions used globally across educational institutions, research centers, and oil companies.
While not a traditional database vendor, Esimtech’s drilling, well control, and well logging simulators play a critical role in:
- Standardizing field data interpretation
- Improving operator competency
- Reducing human-factor data errors
- Supporting realistic scenario-based analysis
- Preparing personnel to work with modern digital systems
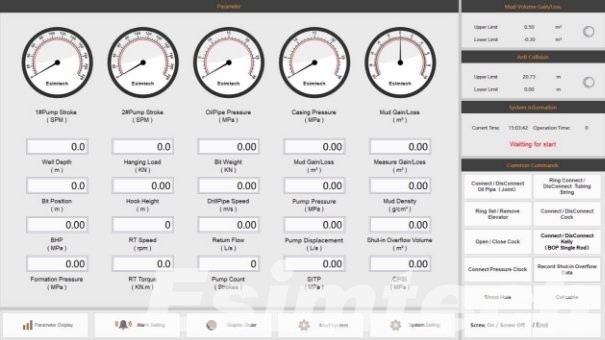
For example, the Well Logging Simulator helps users gain hands-on experience with multi-format data, interpretation techniques, and workflow organization—skills that directly contribute to better data quality in real field operations.
FAQ
1. What types of data does oil and gas data management software handle?
Typical datasets include seismic files, drilling logs, production data, geological surveys, sensor streams, and compliance records.
2. How is data management different from data analytics?
Data management ensures data quality, structure, and accessibility.
Analytics uses that managed data to generate insights and predictions.
3. Why is data quality critical in oilfield operations?
Inaccurate data can lead to safety hazards, incorrect drilling decisions, reservoir misinterpretation, and costly downtime.
4. How does AI enhance oil and gas data workflows?
AI improves pattern recognition, anomaly detection, predictive maintenance, and real-time optimization—provided the underlying data is accurate and well-managed.
Conclusion
Data management moves into the core with evolving oil and gas operations. Quality data speeds up decisions, minimizes operational risks, satisfies regulators, optimizes production in the long run. Organizations that invest in modern data management and build technical muscle with advanced training and simulation solutions stand among the future leaders in the industry.