The Use of Coiled Tubing for Hydraulic Fracturing and Acidizing
Coiled tubing has emerged as an essential component of the modern oil and gas well interventions, particularly for stimulation techniques like hydraulic fracturing or acidizing. The ability to deploy continuous, flexible tubing into live wells without the need for a conventional workover rig has revolutionized how operators manage downhole activities. This article explains the use of coiled tubing for hydraulic fracturing and acidizing, its main advantages, simulations used for optimizing its performance, challenges and solutions in coiled tubing used for hydraulic fracturing and acidizing
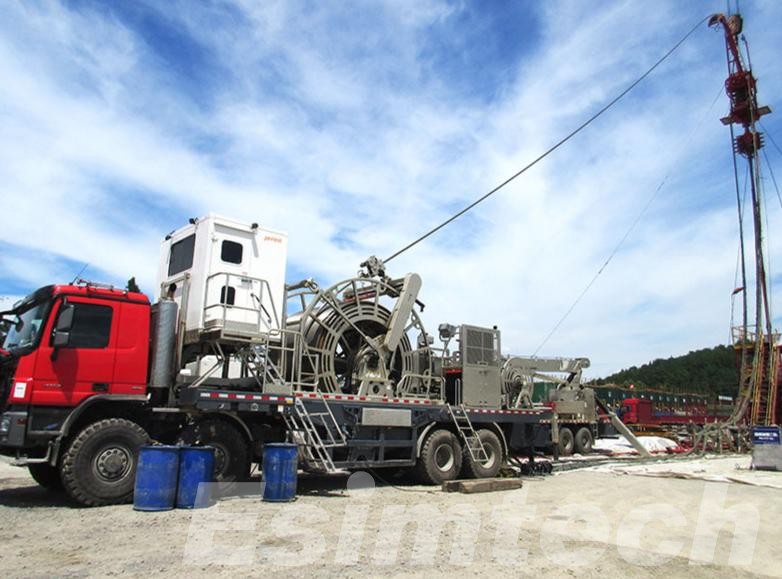

What is Coiled Tubing
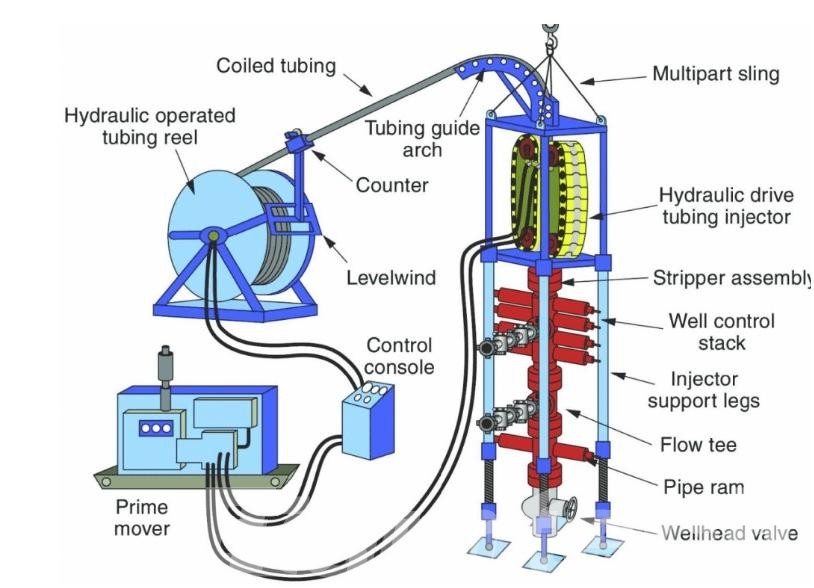
Coiled tubing is a lengthy continuous length of a small diameter steel pipe that is wound on a spool. It is placed into wells to perform a variety of tasks that require intervention without halting production. Because it is able to be removed and inserted at any time, pressure tube reduces downtime and improves flexibility.
Key Components
| Component | Description |
| Coiled Tubing Reel | A large spool which is used to store and distribute the continuous length of tubing coiled. |
| Injector Head | Mechanism that grasps and pulls the tubing that is coiled through or out of the bore. |
| Control Cabin | The enclosed area houses the control systems as well as operator interfaces to manage CT operations. |
| Power Unit | Mechanical power (usually electric or hydraulic) to control the injector as well as other systems. |
| Pressure Control Equipment | Included are Blowerout Preventers (BOPs) along with stripper assemblies that maintain pressure and guarantee security during operations. |
| Hydraulic Power Pack | The system supplies the hydraulic pressure of the various elements within the CT unit. |
| Monitoring and Control Systems | It includes cameras, sensors and computerized controls that control CT parameters like speed, tension and pressure. |
| Wellhead Interface | The CT unit is connected CT device to the head of well. This ensures an airtight and sealed entry point for tubing. |
| Tubing Guide | It guides the tubing through the process of letting it into and out of the wellbore and reel in order to stop damage and Kinking. |
| Fluid Injection System | Control valves and pumps for injecting fluids, such as acid or fluids for fracturing when performing CT operations. |
Key Benefits of Using Coiled Tubing in Hydraulic Fracturing
Hydraulic fracturing is essential in unlocking hydrocarbons from tight and unconventional reservoirs. As the industry shifts towards more complex wells and multiple stage stimulation, Coiled tubing is a crucial facilitator of more effective and controlled fracturing operations. It offers unmatched flexibility and the capability to operate under the live well conditions, coiled tubing significantly enhances both operational performance and economic returns.

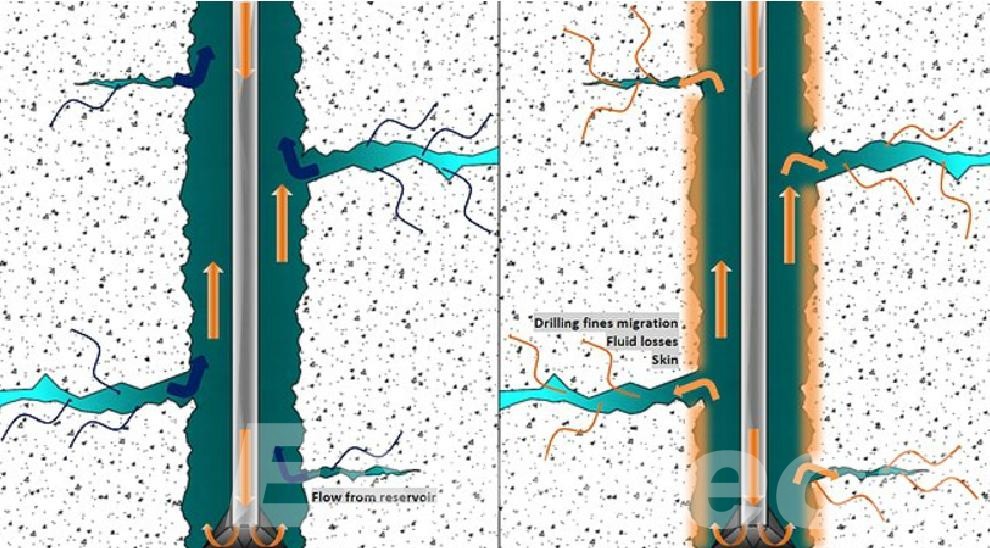
Live Well Access Without Killing the Well
One of the major benefits of coiled tubing is its capability to carry out tasks in live wells which eliminates the necessity of closing or destroying the well. This feature preserves the integrity of reservoirs is a great way to reduce damage to formations and prevents loss of fluid. In turn, operators can ensure that pressure conditions are maintained within the wellbore while avoiding the risks and expenses of conventional well interventions.
Precision in Multistage Fracturing
Coiled tubing can be used to provide high-quality well stimulation. By using bottomhole assemblies with tools such as shift tools and abrasive jet perforators as well as sliding sleeves. Operators are able to select and treat specific areas with a high degree of accuracy. This specialized access will ensure that each stage is given the most effective treatment, increasing the overall efficiency of the reservoir and the hydrocarbon recovery.
Reduced Fracturing Time and Lower Costs
Since coiled tubing doesn’t require the connecting and disconnecting of pipe joints, the process is streamlined and the time to rig-up and rig-down is reduced. The capability of performing continuous operations in multiple stages drastically reduces the total time for fracturing. These efficiency gains translate into savings on the equipment, labor and logistics.
Real-Time Downhole Monitoring and Control
Modern coiled tubing systems are usually coupled with fiber-optic sensors, or downhole telemetry instruments. These systems offer real-time information regarding parameters like the temperature, pressure and flow rates throughout the process of fracturing. This data allows instant adjustments, which improves the accuracy of treatment, reducing risk and enhancing decision-making at the speed of.
Dual Role: Fracturing and Post-Frac Cleanout
In addition to providing the fracturing treatment, coiled tubing is typically used right away following the treatment for cleaning operations. It is capable of removing any residual proppant, sand, and other fluids that could impede production flow. Dual capability eliminates the necessity of transferring separate equipment, reduces time and facilitates an easier transition into this phase of production.
Compact Footprint and Enhanced Safety
Coiled tubing units have less space when compared to traditional workover or drilling rigs. This is especially beneficial in areas that are sensitive to the environment or in areas that have small space. Furthermore, fewer workers and less equipment on the ground help to improve the safety of those at the site.
Suitability for Complex Well Geometries
The flexibility and length of coiled tube make it ideal for maneuvering through long or deviated horizontal wellbores. In contrast to joined pipe, coiled tubing will keep more contact with the wellbore in high-angle or extended-reach wells and ensures the proper positioning of fluids for treatment as well as tools.
Seamless and Continuous Operations
Coiled tubing-based hydraulic fracturing enables continuous operations across multiple stages, without having to take out of the well between stages. This seamless procedure eliminates unnecessary delays and enhances the consistency of the treatment which is particularly beneficial for wells with high-stage count and long laterals.

Key Advantages of Using Coiled Tubing in Acidizing
Acidizing is an essential well stimulation technique that aims at increasing the permeability the formations containing hydrocarbons by removing damages and stimulating production zones. Coiled tubing is becoming the most preferred method of acid placement due to its flexibility, precision and operational efficiency.
Precise Acid Placement
One of the major advantages of the coiled tubing when acidizing is that it can give acids precisely in the targeted region inside the wellbore. In horizontal, deviated, and horizontal wells, the use of coiled tubing permits precise depth-targeting and improves the effectiveness of treatment while reducing the risk of over-acidizing or triggering unwanted intervals. This is especially beneficial for reservoirs that have thin or uneven layers.
Live Well Operations
Coiled tubing can be put into wells and not kill production, which allows acidizing processes inside live wells. This minimizes the risk of damage to formation that can result due to the introduction of kill fluids. It also permits operators to maintain flow and pressure conditions, which ensures the integrity of wells throughout the process.
Improved Efficiency and Time Savings
Coiled tubing acidizing can eliminate the requirement for setting up and taking down, providing a smooth and continuous process. In matrix acidizing and other stimulation tasks, coiled tubing reduces non-productive time (NPT), accelerates treatment schedules, and enhances overall operational efficiency–especially in remote or offshore locations where logistics are challenging.
Zonal Isolation and Selective Stimulation
With the help of coiled tubing operators can employ downhole equipment like straddles, packers assemblies and jetting nozzles to treat and isolate specific zones. This allows for the selective stimulation of acids that is crucial for maximizing contact with reservoirs in multizone wells, or for activating certain areas in wells that are older, without impacting neighboring formations.
Real-Time Monitoring and Treatment Control
Coiled tubing that is modern may include temperature, pressure as well as flow sensors, which allow the operators to track the conditions of treatment in real-time. This permits on-the-fly adjustments to levels of acid or pumping rates increasing the precision and security of the process and reducing the chance of failure in treatment.
Reduced Surface Footprint and Enhanced Safety
In comparison to traditional acidizing systems which require bigger rigs and large infrastructures on the surface, coiled tubing units are small and easy to move particularly in tight spaces. Less personnel and less equipment means less HSE risks as well as faster process restoration following treatment.
Dual Functionality for Post-Acid Cleanout
Once acidized, this tube can be reused quickly to clean out post-treatment processes, like the removal of byproducts from reaction and debris or precipitates. This improves the cleanliness of wellbore vital to reaping the full benefits of the acidizing process as well as making sure that the process is long-lasting and efficient.
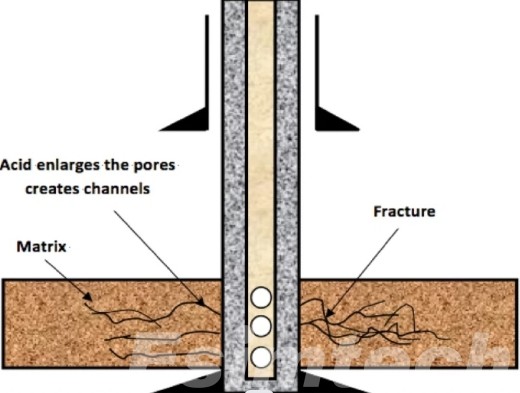
Applicability in Both Matrix and Fracture Acidizing
Coiled tubing can be effective in both matrix acidizing (low-pressure treatment to dissolve the damage caused by formation) and fracture acidizing (high-pressure injection to allow for the opening and etching of fresh pathways). In both instances, coiled tubing provides superior control, decreasing the chance of accidental stimulation, and enhancing the effectiveness of treatment in a variety of reservoir conditions.

How Simulation Technology is Used for Coiled Tubing Applied in Hydraulic Fracturing and Acidizing
Simulation technology plays a growing important role in optimizing the coiled tubing process in hydraulic fracturing and acidizing. Due to the complexity of fluid dynamics, well geometries and downhole conditions, well intervention simulations allow engineers to develop more efficient, safer and precise operations.
Mechanical and Fatigue Analysis
Coiled tubing is subject to massive mechanical stress as a result of constant stretching, pressure cycling and contact with wellbore surface. Coiled tubing simulations model the mechanical and fatigue behaviour of coiled tubing strings in various operating conditions, allowing engineers to anticipate the points of failure and plan preventive maintenance. This increases the lifespan of the tubing and lowers the chance of costly downhole problems.

Hydraulic Modeling of Fluid Flow
Simulation tools model the flow of fluid inside and outside the tubing that is coiled, including velocity profiles, pressure drops and multiphase flow behaviour during acidizing or fracturing. This aids in maximizing the pumping rate and pressure settings as well as fluid compositions in order to ensure efficient crack propagation or acidization without causing damage or erosion to the tubing or wellbore.
Wellbore Trajectory and Coil Tubing Reach
In horizontal and inclined wells, models are employed to evaluate the capability of coiled tubing to get to the desired zones without excessive friction or buckling. Mechanical models, coupled with contact and friction analysis aid in designing the tubing string and other operational variables that maximize reach and assure the smoothest deployment.

Zonal Isolation and Treatment Optimization
In the case of multistage fracturing or acidizing, simulation software is able to model the interactions between tubes that are coiled, such as sleeves, packers, or perforating guns with formation. This allows for the optimization of zones of isolation and treatment sequences in order to increase effectiveness of reservoir stimulation and decrease cross-flows of fluid.
Thermal and Corrosion Analysis
Simulations can predict temperature variations as well as chemical interactions within the well throughout acidizing. This helps engineers to assess the risk of corrosion and thermal stress in the coiled tubing string and bottomhole assemblies. These findings aid in the selection of material and operational parameters, which can improve the durability of equipment.
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Control
Advanced fracturing and acidizing simulators can be integrated live data streams from real time coiled tube sensors, which allows dynamic simulation and control that is predictive when acidizing or fracturing. Operators can model the outcomes of changing parameters in real-time, increasing the precision of treatment while decreasing operational risks.

Challenges and Solutions in Coiled Tubing for Hydraulic Fracturing and Acidizing
| Challenges | Description | Solutions |
| Tubing Fatigue and Wear | Continuous bending, pressure cycling and the harshness of fluids result in fatigue and damage | Make use of high-strength material as well as fatigue monitoring software and a proper management of lifecycles |
| Limited Reach in Long Horizontal Wells | Buckling and friction can prevent full-depth access | Utilize downhole tractors, friction reduction devices or coiled tubing that is optimized for string designs |
| Pressure and Temperature Limitations | Coiled tubing might not be able to be able to withstand extreme conditions in the downhole | Utilize thicker-walled tubing, high-tech alloys, or dual-coiled tubing strings |
| Inefficient Acid Placement in Complex Zones | The risk of distribution that is uneven within multizone reservoirs | Use tools for zonal isolation, such as inflatable packers or straddles to target acidification |
| Limited Real-Time Data Acquisition | Inaccurate downhole data during treatment | Integrate coiled tube with fiber-optic sensors or memory/logging devices to monitor in real-time |
| Sand/Proppant Blockages During Fracturing | Residual material may impede the movement of coiled tubing and also production flow | Use cleaning tools (e.g. jetting nozzles, ecoil tool for reaming) post-frac |
| Corrosion resulting from Acidic Fluids | Acidizing fluids can cause corrosion to the coiled tubing as well as BHA components | Utilize corrosion-resistant material (e.g. Inconel, Inconel, and coated tubing) as well as apply corrosion inhibitants |
| Operational Safety in High-Pressure Environments | Risques to equipment and personnel in live operations | Make sure you enforce strict pressure control and use pressure relief valves and abide by improved HSE procedures. |
| Tool Deployment Complexity in Multistage Operations | The difficulty in managing the toolstrings and transitions between stages | Utilize modular BHAs, real-time Telemetry, and automated tubing injectors to create smoother stages |
| Logistical Challenges in Remote or Offshore Locations | Transporting and operating coiled tube units within constrained space | Utilize small coiled tubing units or modular equipment as well as planned staging for a smoother process of the process of mobilization |

Final Thoughts
Coiled tubing is essential in enhancing the efficiency, precision, and safety of hydraulic fracturing and acidizing operations. Its capability to perform live well interventions, provide targeted treatments, and facilitate real-time monitoring make it critical for today’s increasingly complex reservoirs.

