How Digital Oilfields are Changing Oil & Gas Jobs
The oil and gas industry is currently experiencing a profound transformation due to digital technologies, with digital oilfields that combine IoT, AI, big data analytics, and automation creating significant disruption in how things operate while opening up opportunities and challenges for workers.
This article investigates how digital oilfields are impacting jobs in the oil and gas sector, the challenges employees are enduring as a result, and what the future may hold for employment in this emerging field.

The Shift from Traditional to Digital Oilfield Operations
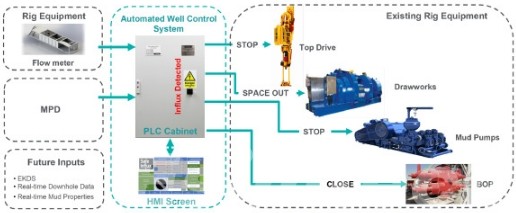
Oil and gas industry operations are currently experiencing a major transformation with the rise of digital oilfields, marking an escape from labor-intensive practices of yesteryear. Oilfield activities had long relied heavily on manual inspections, on-site monitoring, and reactive decision-making processes that often required manual intervention for inspections or monitoring and decisions to be taken, which proved inefficient in practice as they took considerable time, cost, and often led to human mistakes and time delays.

Digital oilfields are revolutionizing this dynamic by employing advanced technologies like real-time data analytics, Internet of Things sensors, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence in operations. These tools allow operators to remotely monitor assets while anticipating failures before they occur and making data-driven decisions that boost productivity while decreasing downtime, for instance, through automated drilling systems and predictive maintenance tools for more precise operations and increased safety.
This shift goes far beyond simply replacing old tools with new ones; rather, it represents a complete transformation in oil and gas operations. By streamlining workflows and increasing operational visibility, digital oilfields provide greater efficiencies, lower operating costs, improved environmental compliance, and environmental benefits for oil production companies.
As companies invest more heavily in digital infrastructure solutions, traditional oilfield models are quickly being transformed into smarter systems offering increased connectivity that are sustainable, while setting the groundwork for energy production in the next era.
How Digital Oilfields Are Impacting Oil & Gas Jobs?

The advent of digital oilfields has triggered a profound transformation in the oil and gas job landscape. Here is my take on how these digital advancements are impacting employment, focusing on the evolving job requirements and emerging opportunities.
Automation of traditional roles
Now, more jobs that formerly required manual labor or monitoring tasks are becoming automated. For instance, workers had previously had to traverse vast oilfield terrains regularly checking well pressure gauges by hand while recording flow rates manually before manually entering data into cumbersome paper ledgers - an effort-consuming and error-prone process which consumed much time and resources.
However, with IoT sensors now integrated into our operations, these operations have been significantly simplified. These sensors can be placed onto equipment like pumps, valves and pipelines and continuously collect real - time data about temperature, vibration levels and fluid levels for transmission directly into a central system, eliminating manual data collection processes as well as decreasing the workforce required for routine tasks such as this one.
Emergence of new job opportunities
Digital transformation in oilfields has resulted in many new job roles and functions. Data scientists are in high demand as they must sift through vast volumes of sensor-generated information in order to spot patterns, trends and correlations that help companies make data-driven decisions regarding production optimization, reservoir management and cost reduction strategies.
AI and ML engineers develop intelligent algorithms. These intelligent programs can anticipate equipment failure weeks in advance by analyzing historical data and current operational conditions, helping companies plan preventive maintenance schedules to eliminate downtime costs. Furthermore, with digital oilfields becoming more connected through networks comes increased cyberattack risk that necessitates cybersecurity experts who can protect critical infrastructure as well as sensitive data.

Redefinition of required skills
Digital transformation isn't simply about swapping out one job with another; rather, it involves drastically revamping the required skill sets of workers in each industry. Now more than ever before, workers in particular industries such as oilfield need a blend of technical know-how and digital knowledge to thrive within them. A mechanical engineer working within such an environment must possess not only knowledge about oilfield equipment mechanics but also adept in using digital tools for monitoring, data analysis, and predictive maintenance of that same equipment.
Similar to technicians, technicians must possess both physical and digital troubleshooting expertise for troubleshooting equipment and related digital systems. Furthermore, soft skills like adaptability, critical thinking and team collaboration are highly valued as digital oilfield operations often necessitate collaboration across departments like engineering production IT analytics.
What are the Challenges for Workforce?

Transitioning to digital oilfields unquestionably brings many advantages; however, this also presents workers in the oil and gas sector with significant challenges.
- One of the greatest problems companies are currently facing is a skills gap. As businesses integrate advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT into their operations, there's a growing need for employees capable of operating and understanding these systems; however, many traditional field operators may lack digital literacy to transition effectively into this digitalized age.
- Upskilling and reskilling have become essential. Companies must invest in training programs to assist employees in adapting to roles requiring data analysis, software proficiency, and real-time decision-making. But this shift doesn't just involve learning new tools; rather, field workers must now think more like technicians and analysts when considering digital inputs as contributing factors toward operational outcomes.
- Job displacement is also an area of great concern; automation and remote monitoring technologies are increasingly replacing manual, on-site jobs with automation or remote monitoring technologies, while digital transformation offers new opportunities but may lead to layoffs of roles deemed outdated; this dynamic can create uncertainty among workers in regions heavily reliant on oil and gas employment opportunities.
- Attracting digitally adept talent presents another obstacle. Younger professionals with tech knowledge tend to gravitate toward industries perceived as more modern or sustainable; oil and gas must compete for this talent by reinventing its image and providing clear career pathways within emerging digital roles - something the oilfield sector must address for an inclusive transition into its digital future.
Future of Oil & Gas Employment: What Can We See?
As automation, data analytics and artificial intelligence become key elements of operations, industries are transitioning away from labor-intensive roles towards technology-focused careers. While traditional jobs may decline due to technological changes, new opportunities arise that demand different skill sets such as digital infrastructure management, data science research projects, remote operations management or cybersecurity expertise.

This transformation doesn't portend job losses; rather, it marks a change in roles needed. Professionals with expertise bridging engineering with digital technology will become even more in demand; for instance digital project managers, data analysts, and automation specialists have quickly become essential assets at oil and gas firms looking to remain competitive.
To address this shift, the industry needs to invest in workforce development through training, reskilling and collaboration with educational institutions. Companies who proactively support employee transition into digital roles will be better placed for long-term success; adaptability and constant learning are keys in such an evolving landscape - the oil and gas workforce of tomorrow must be more diverse, tech savvy, resilient as it meets both energy demands and sustainability goals simultaneously in a rapidly digitizing world.
All in All
The move towards digital oilfield operations represents an historic transformation for the oil and gas sector. While adopting digitalization requires adapting workforce practices and restructuring jobs, its rewards in terms of improved safety, increased efficiency, reduced environmental impact are undeniable. Adopting digitalization doesn't just involve adopting new technologies but rather creating future-ready employees capable of managing complex digital oilfield environments as the industry expands and changes; successful strategies for workforce development and technological integration are vital if growth and competition in global markets is to continue.