How Well Intervention Simulation Training Reduces Non-Productive Time
During the entire life cycle of an oil and gas well, Well Intervention (well repair/underground intervention operations) is a crucial step for restoring production capacity, extending well life, and addressing wellbore issues. However, this stage is also one of the scenarios with high incidence of non-productive time (NPT).
As well conditions become more complex and operation costs rise, an increasing number of operators are turning to Well Intervention simulation training (simulation-based training) to identify risks and optimize processes before the operation, thereby reducing NPT from the source.

What Is Non-Productive Time (NPT) in Well Intervention?
NPT (Non-Production Time) refers to the time during which operations are halted or efficiency declines due to unplanned events. This is commonly observed in the following situations:
- Failure or stuck of tool insertion
- Well control incidents or abnormal pressure responses
- Re-work due to incorrect operation procedures
- Collaborative errors among multiple professional teams
- Decision delays in complex well conditions
In high-cost well repair operations, every reduction of 1 hour in NPT often means direct savings of tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of dollars. And NPT typically accounts for 15% to 30% of the total operation time, making it the part with the most potential for optimization.
Common Causes of NPT in Well Intervention Operations
Human Error and Lack of Operational Experience
- Novice engineers lack understanding of complex well conditions
- Incorrect sequence of operations or parameter settings
- Inadequate emergency response skills
- Judgment at key nodes relies on personal experience
Incomplete Understanding of Well Conditions
- Insufficient understanding of wellbore structure and completion methods
- Failure to accurately predict downhole risks (pressure difference, sediment, aging casing)

Poor Cross-Functional Collaboration
- The information of well repair engineers, well control personnel and platform operators is not synchronized.
- Communication at key nodes is delayed
- The decision-making chain is too long, resulting in an increase in waiting time.
Slow Response to Abnormal Well Conditions
- Well blowout, pressure surge, tool malfunction
- The on-site personnel could only "do while thinking", with slow response and high risks
- Inexperienced in emergency handling procedures, with delayed response
What Is Well Intervention Simulation Training?
Well Intervention simulation training is a highly realistic training system built based on real wellbore models, operation equipment and process flows, used for:
- Reproducing the actual well intervention operation process
- Simulating normal and abnormal working conditions
- Training operational skills, decision-making abilities and teamwork
Its core objective is not "showcasing the process", but rather to anticipate and address errors and risks before entering the field.
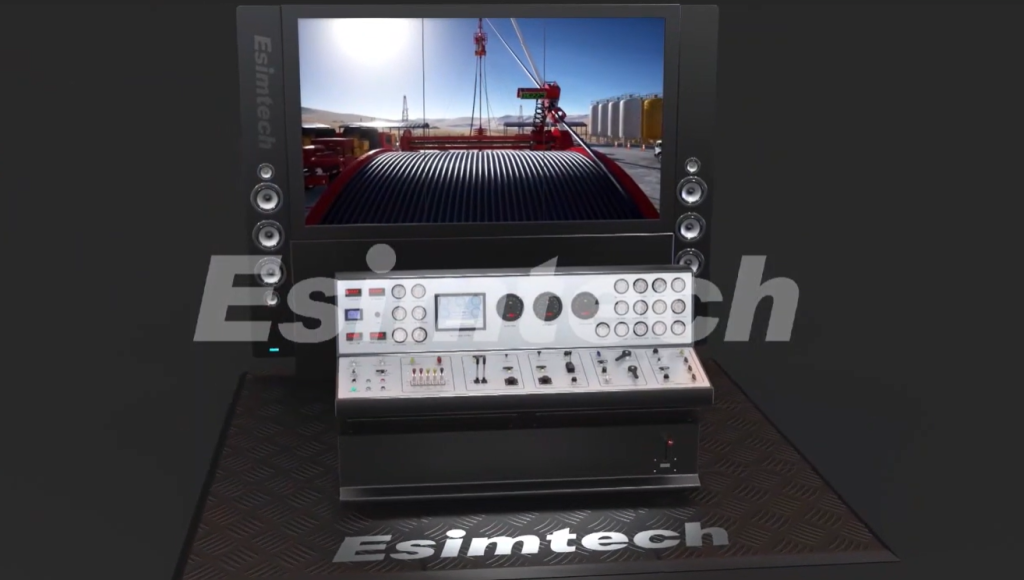

How Simulation Training Reduces NPT in Well Intervention
Identifying High-Risk Operations Before Field Execution
By simulating the entire operation process, the team can identify issues in advance:
- The key steps such as tool insertion, retrieval, plugging, acidizing, etc.
- Identifying process bottlenecks in the virtual environment
- Optimizing the operation sequence and reducing on-site trial and error
Effect: Reducing NPT due to unreasonable process, and reducing waiting time caused by process adjustments
Improving Response Speed to Abnormal Well Conditions
The simulation system can create various emergency scenarios:
- well blowout / abnormal pressure
- tool sticking
- abnormal changes in flow rate and wellhead parameters
Through repeated practice, engineers develop a reflexive decision-making ability.
Effect: Shorten the response time for emergencies, reduce the long-term shutdown caused by the expansion of the accident, and the time spent waiting for remote expert decisions.

Reducing Human Error Through Repetitive Practice
Simulation training helps engineers:
- Standardizes operation procedures
- Makes understanding of key parameters (pressure, displacement, tension) more intuitive
- Newcomers can quickly reach the level of being able to operate independently
Effect: Reduces tool damage and operation interruptions caused by incorrect operations
Enhancing Multi-Role Team Coordination
The Well Intervention simulator typically supports:
- Simultaneous training of multiple roles (well drilling engineers, well control personnel, platform operators)
- Unified data view and operation rhythm
- Simulation of complex collaborative scenarios
Effect: Reduces waiting and decision-making delays caused by information incoherence
Optimizing Operational Decisions to Avoid Trial-and-Error NPT
By simulating different operation plans, the following can be compared:
- The operation time of different well repair schemes
- Risk levels and success rates
- The impact of key parameter adjustments on the results
Effect: Reduce the hidden NPT caused by "trial-and-error" decision-making, and thereby select the scheme with the lowest NPT and the most controllable risks for on-site implementation.
Simulation Training vs Traditional On-the-Job Learning
| Comparison | Traditional method | Well Intervention simulation training |
| Risk exposure Cost | Only in the field | Early exposure during training stage Low |
| Cost of Error | High | Low |
| Learning Speed | Actual work stoppage | Virtual zero loss |
| NPT Controllability | Slow | Quick |
| Quality of Decision-making | Low | High |
| Comparison | Relying on experience | Data and exercise support |
Well Intervention Operations That Benefit Most from Simulation Training
- Well workover and completion intervention
- Pressure-bearing operation (Live Well Intervention)
- Complex wells (horizontal wells, old wells, HPHT wells)
- Key wells or high-production wells
- Before the establishment of a new team or the application of new technologies
Conclusion
Well Intervention simulation training does not replace on-site experience; instead, it shifts the control of NPT (Non-Production Time) to before the operation.
Through systematic simulation training, operators can:
- Identify high NPT risks in advance
- Improve team operational consistency
- Shorten abnormal response time
- Significantly reduce the overall NPT ratio in well workovers
In the current oil and gas environment that prioritizes "cost reduction and efficiency improvement + safety and compliance", Well Intervention simulation training has shifted from an "optional" measure to a "core capability building" aspect.